Transport Layer Protocols-
There are mainly two transport layer protocols that are used on the Internet-
- Transmission Control Protocol (TCP)
- User Datagram Protocol (UDP)
In this article, we will discuss about User Datagram Protocol (UDP).
Learn about Transmission Control Protocol.
UDP Protocol-
- UDP is short for User Datagram Protocol.
- It is the simplest transport layer protocol.
- It has been designed to send data packets over the Internet.
- It simply takes the datagram from the network layer, attaches its header and sends it to the user.
Characteristics of UDP-
- It is a connectionless protocol.
- It is a stateless protocol.
- It is an unreliable protocol.
- It is a fast protocol.
- It offers the minimal transport service.
- It is almost a null protocol.
- It does not guarantee in order delivery.
- It does not provide congestion control mechanism.
- It is a good protocol for data flowing in one direction.
Need of UDP-
- TCP proves to be an overhead for certain kinds of applications.
- The Connection Establishment Phase, Connection Termination Phase etc of TCP are time consuming.
- To avoid this overhead, certain applications which require fast speed and less overhead use UDP.
UDP Header-
The following diagram represents the UDP Header Format-
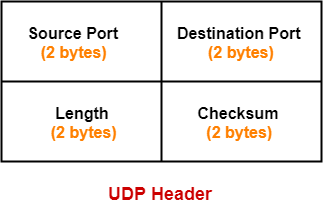
1. Source Port-
- Source Port is a 16 bit field.
- It identifies the port of the sending application.
2. Destination Port-
- Destination Port is a 16 bit field.
- It identifies the port of the receiving application.
3. Length-
- Length is a 16 bit field.
- It identifies the combined length of UDP Header and Encapsulated data.
| Length = Length of UDP Header + Length of encapsulated data |
4. Checksum-
- Checksum is a 16 bit field used for error control.
- It is calculated on UDP Header, encapsulated data and IP pseudo header.
- Checksum calculation is not mandatory in UDP.
Applications Using UDP-
Following applications use UDP-
- Applications which require one response for one request use UDP. Example- DNS.
- Routing Protocols like RIP and OSPF use UDP because they have very small amount of data to be transmitted.
- Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP) uses UDP to send very small sized files.
- Broadcasting and multicasting applications use UDP.
- Streaming applications like multimedia, video conferencing etc use UDP since they require speed over reliability.
- Real time applications like chatting and online games use UDP.
- Management protocols like SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) use UDP.
- Bootp / DHCP uses UDP.
- Other protocols that use UDP are- Kerberos, Network Time Protocol (NTP), Network News Protocol (NNP), Quote of the day protocol etc.
Important Notes-
Note-01:
| Size of UDP Header= 8 bytes |
- Unlike TCP header, the size of UDP header is fixed.
- This is because in UDP header, all the fields are of definite size.
- Size of UDP Header = Sum of the size of all the fields = 8 bytes.
Note-02:
| UDP is almost a null protocol. |
This is because-
- UDP provides very limited services.
- The only services it provides are checksumming of data and multiplexing by port number.
Note-03:
| UDP is an unreliable protocol. |
This is because-
- UDP does not guarantee the delivery of datagram to its respective user (application).
- The lost datagrams are not retransmitted by UDP.
Note-04:
| Checksum calculation is not mandatory in UDP. |
This is because-
- UDP is already an unreliable protocol and error checking does not make much sense.
- Also, time is saved and transmission becomes faster by avoiding to calculate it.
It may be noted-
- To disable the checksum, the field value is set to all 0’s.
- If the computed checksum is zero, the field value is set to all 1’s.
Note-05:
| UDP does not guarantee in order delivery. |
This is because-
- UDP allows out of order delivery to ensure better performance.
- If some data is lost on the way, it does not call for retransmission and keeps transmitting data.
Note-06:
| Application layer can perform some tasks through UDP. |
Application layer can do the following tasks through UDP-
- Trace Route
- Record Route
- Time stamp
When required,
- Application layer conveys to the UDP which conveys to the IP datagram.
- UDP acts like a messenger between the application layer and the IP datagram.
Also Read- TCP Header | IPv4 Header
PRACTICE PROBLEMS BASED ON UDP HEADER-
Problem-01:
Which field is optional in UDP?
- Checksum
- Destination port
- Length
- None
Solution-
- Checksum calculation is not mandatory in UDP.
- Thus, Option (A) is correct.
Problem-02:
The pseudo header of IP is used in-
- Only TCP
- Only UDP
- Both TCP and UDP
- None
Solution-
- IP Pseudo header is used in both TCP and UDP while calculating checksum.
- Thus, Option (C) is correct.
Problem-03:
Broadcasting applications like WHOD (who daemon on UNIX) uses what transport layer protocol?
- TCP
- UDP
- Either TCP or UDP
- IGMP
Solution-
- Broadcasting and multicasting applications use UDP.
- Thus, Option (B) is correct.
To gain better understanding about UDP Header,
Next Article- Application Layer Protocols
Get more notes and other study material of Computer Networks.
Watch video lectures by visiting our YouTube channel LearnVidFun.

