Three Address Code-
| Three Address Code is a form of an intermediate code. |
The characteristics of Three Address instructions are-
- They are generated by the compiler for implementing Code Optimization.
- They use maximum three addresses to represent any statement.
- They are implemented as a record with the address fields.
General Form-
In general, Three Address instructions are represented as-
| a = b op c |
Here,
- a, b and c are the operands.
- Operands may be constants, names, or compiler generated temporaries.
- op represents the operator.
Examples-
Examples of Three Address instructions are-
- a = b + c
- c = a x b
Common Three Address Instruction Forms-
The common forms of Three Address instructions are-
1. Assignment Statement-
| x = y op z and x = op y |
Here,
- x, y and z are the operands.
- op represents the operator.
It assigns the result obtained after solving the right side expression of the assignment operator to the left side operand.
2. Copy Statement-
| x = y |
Here,
- x and y are the operands.
- = is an assignment operator.
It copies and assigns the value of operand y to operand x.
3. Conditional Jump-
| If x relop y goto X |
Here,
- x & y are the operands.
- X is the tag or label of the target statement.
- relop is a relational operator.
If the condition “x relop y” gets satisfied, then-
- The control is sent directly to the location specified by label X.
- All the statements in between are skipped.
If the condition “x relop y” fails, then-
- The control is not sent to the location specified by label X.
- The next statement appearing in the usual sequence is executed.
4. Unconditional Jump-
| goto X |
Here, X is the tag or label of the target statement.
On executing the statement,
- The control is sent directly to the location specified by label X.
- All the statements in between are skipped.
5. Procedure Call-
| param x call p return y |
Here, p is a function which takes x as a parameter and returns y.
PRACTICE PROBLEMS BASED ON THREE ADDRESS CODE-
To solve the problems, Learn about the Precedence Relations and Associativity of Operators.
Problem-01:
Write Three Address Code for the following expression-
a = b + c + d
Solution-
The given expression will be solved as-
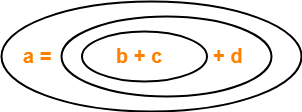
Three Address Code for the given expression is-
(1) T1 = b + c
(2) T2 = T1 + d
(3) a = T2
Problem-02:
Write Three Address Code for the following expression-
-(a x b) + (c + d) – (a + b + c + d)
Solution-
Three Address Code for the given expression is-
(1) T1 = a x b
(2) T2 = uminus T1
(3) T3 = c + d
(4) T4 = T2 + T3
(5) T5 = a + b
(6) T6 = T3 + T5
(7) T7 = T4 – T6
Problem-03:
Write Three Address Code for the following expression-
If A < B then 1 else 0
Solution-
Three Address Code for the given expression is-
(1) If (A < B) goto (4)
(2) T1 = 0
(3) goto (5)
(4) T1 = 1
(5)
Problem-04:
Write Three Address Code for the following expression-
If A < B and C < D then t = 1 else t = 0
Solution-
Three Address Code for the given expression is-
(1) If (A < B) goto (3)
(2) goto (4)
(3) If (C < D) goto (6)
(4) t = 0
(5) goto (7)
(6) t = 1
(7)
Also Read- More Problems On Three Address Code
To gain better understanding about Three Address Code,
Download Handwritten Notes Here-
Next Article- Quadruples, Triples & Indirect Triples
Get more notes and other study material of Compiler Design.
Watch video lectures by visiting our YouTube channel LearnVidFun.


