Transmission Control Protocol-
Before you go through this article, make sure that you have gone through the previous article on TCP in Networking.
We have discussed-
- TCP establishes an end to end connection between the sender and receiver.
- This connection is established before exchanging the data.
- TCP connection is reliable and ensures in order delivery.
Also Read- TCP Header
In this article, we will discuss how a TCP connection is established.
3 Way Handshake-
| Three Way Handshake is a process used for establishing a TCP connection. |
Consider-
- Client wants to establish a connection with the server.
- Before Three Way Handshake, both client and server are in closed state.
TCP Handshake involves the following steps in establishing the connection-
Step-01: SYN-
For establishing a connection,
- Client sends a request segment to the server.
- Request segment consists only of TCP Header with an empty payload.
- Then, it waits for a reply segment from the server.

Request segment contains the following information in TCP header-
- Initial sequence number
- SYN bit set to 1
- Maximum segment size
- Receiving window size
1. Initial Sequence Number-
- Client sends the initial sequence number to the server.
- It is contained in the sequence number field.
- It is a randomly chosen 32 bit value.
2. SYN Bit Set To 1-
Client sets SYN bit to 1 which indicates the server-
- This segment contains the initial sequence number used by the client.
- It has been sent for synchronizing the sequence numbers.
Also Read- TCP Sequence Number
3. Maximum Segment Size (MSS)-
- Client sends its MSS to the server.
- It dictates the size of the largest data chunk that client can send and receive from the server.
- It is contained in the Options field.
4. Receiving Window Size-
- Client sends its receiving window size to the server.
- It dictates the limit of unacknowledged data that can be sent to the client.
- It is contained in the window size field.
Step-02: SYN + ACK-
After receiving the request segment,
- Server responds to the client by sending the reply segment.
- It informs the client of the parameters at the server side.
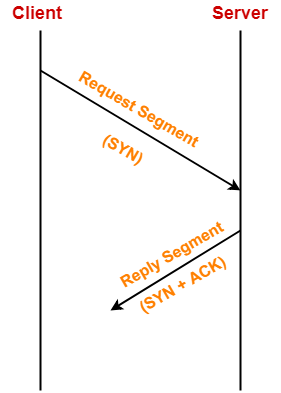
Reply segment contains the following information in TCP header-
- Initial sequence number
- SYN bit set to 1
- Maximum segment size
- Receiving window size
- Acknowledgment number
- ACK bit set to 1
1. Initial Sequence Number-
- Server sends the initial sequence number to the client.
- It is contained in the sequence number field.
- It is a randomly chosen 32 bit value.
2. SYN Bit Set To 1-
Server sets SYN bit to 1 which indicates the client-
- This segment contains the initial sequence number used by the server.
- It has been sent for synchronizing the sequence numbers.
3. Maximum Segment Size (MSS)-
- Server sends its MSS to the client.
- It dictates the size of the largest data chunk that server can send and receive from the client.
- It is contained in the Options field.
4. Receiving Window Size-
- Server sends its receiving window size to the client.
- It dictates the limit of unacknowledged data that can be sent to the server.
- It is contained in the window size field.
5. Acknowledgement Number-
- Server sends the initial sequence number incremented by 1 as an acknowledgement number.
- It dictates the sequence number of the next data byte that server expects to receive from the client.
6. ACK Bit Set To 1-
- Server sets ACK bit to 1.
- It indicates the client that the acknowledgement number field in the current segment is valid.
Step-03: ACK-
After receiving the reply segment,
- Client acknowledges the response of server.
- It acknowledges the server by sending a pure acknowledgement.

With these, a Full Duplex connection is established.
Important Points-
Point-01:
In step-01 and step-02-
- The connection parameters are established for the first side.
- They are acknowledged by the second side.
In step-02 and step-03-
- The connection parameters are established for the second side.
- They are acknowledged by the first side.
Point-02:
| Connection establishment phase consume 1 sequence number of both the sides. |
- Request segment consumes 1 sequence number of the requester.
- Reply segment consumes 1 sequence number of the respondent.
- Pure acknowledgements do not consume any sequence number.
Point-03:
| Pure acknowledgement for the reply segment is not necessary. |
This is because-
- If client sends the data packet immediately, then it will be considered as an acknowledgement.
- It means that in the first two steps only, the full duplex connection is established.
Point-04:
| For all the segments except the request segment, ACK bit is always set to 1. |
This is because-
- For the request segment, acknowledgement number field will always be invalid.
- For all other segments, acknowledgement number field will always be valid.
Point-05:
| Certain parameters are negotiated during connection establishment. |
The negotiation can be on setting the values of following parameters-
- Window size
- Maximum segment size
- Timer values
Point-06:
In any TCP segment,
- If SYN bit = 1 and ACK bit = 0, then it must be the request segment.
- If SYN bit = 1 and ACK bit = 1, then it must be the reply segment.
- If SYN bit = 0 and ACK bit = 1, then it can be the pure ACK or segment meant for data transfer.
- If SYN bit = 0 and ACK bit = 0, then this combination is not possible.
Point-07:
- The combination SYN bit = 0 and ACK bit = 0 is not possible.
- It is because SYN bit = 0 signifies it is not the request segment and reply segment.
- For all other segments, ACK bit is always set to 1.
Point-08:
- Consider sender sends the segments of size greater than MSS of receiver.
- Then, they are first fragmented first at the receiver side.
- It causes an extra overhead.
Point-09:
- There is no dedicated field for sending MSS in TCP header.
- This is because MSS has to informed only once.
- So, if dedicated field would be present, then sending it each time would not be required.
- For this reason, MSS is informed once using Options field.
Also Read- TCP Connection Termination
PRACTICE PROBLEMS BASED ON THREE WAY HANDSHAKE-
Problem-01:
SYN = 0 and ACK = 1 indicates-
- Open connection packet
- Open connection ACK
- Data packet
- ACK packet
Solution-
Options (C) and (D) are correct.
Problem-02:
An acknowledgement by TCP sender guarantees-
- Data has been delivered to the application
- Data has been received by TCP module
- Data has been received by application interface
- None of the above
Solution-
Option (A) is correct.
To gain better understanding about Three Way Handshake,
Next Article- TCP Retransmission
Get more notes and other study material of Computer Networks.
Watch video lectures by visiting our YouTube channel LearnVidFun.