Transaction in DBMS-
“Transaction is a set of operations which are all logically related.”
OR
“Transaction is a single logical unit of work formed by a set of operations.”
Operations in Transaction-
The main operations in a transaction are-
- Read Operation
- Write Operation
1. Read Operation-
- Read operation reads the data from the database and then stores it in the buffer in main memory.
- For example- Read(A) instruction will read the value of A from the database and will store it in the buffer in main memory.
2. Write Operation-
- Write operation writes the updated data value back to the database from the buffer.
- For example- Write(A) will write the updated value of A from the buffer to the database.
Transaction States-
A transaction goes through many different states throughout its life cycle.
These states are called as transaction states.
Transaction states are as follows-
- Active state
- Partially committed state
- Committed state
- Failed state
- Aborted state
- Terminated state
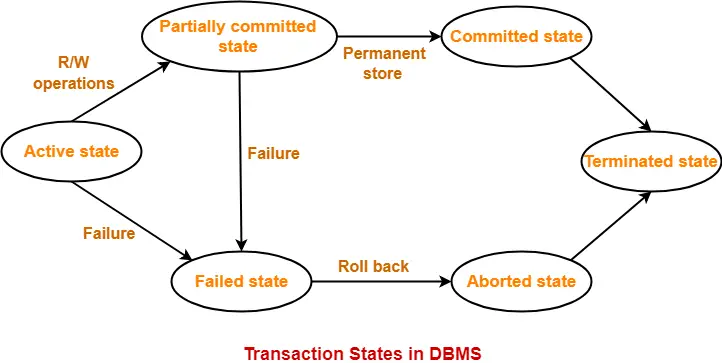
1. Active State-
- This is the first state in the life cycle of a transaction.
- A transaction is called in an active state as long as its instructions are getting executed.
- All the changes made by the transaction now are stored in the buffer in main memory.
2. Partially Committed State-
- After the last instruction of transaction has executed, it enters into a partially committed state.
- After entering this state, the transaction is considered to be partially committed.
- It is not considered fully committed because all the changes made by the transaction are still stored in the buffer in main memory.
3. Committed State-
- After all the changes made by the transaction have been successfully stored into the database, it enters into a committed state.
- Now, the transaction is considered to be fully committed.
NOTE-
- After a transaction has entered the committed state, it is not possible to roll back the transaction.
- In other words, it is not possible to undo the changes that has been made by the transaction.
- This is because the system is updated into a new consistent state.
- The only way to undo the changes is by carrying out another transaction called as compensating transaction that performs the reverse operations.
4. Failed State-
- When a transaction is getting executed in the active state or partially committed state and some failure occurs due to which it becomes impossible to continue the execution, it enters into a failed state.
5. Aborted State-
- After the transaction has failed and entered into a failed state, all the changes made by it have to be undone.
- To undo the changes made by the transaction, it becomes necessary to roll back the transaction.
- After the transaction has rolled back completely, it enters into an aborted state.
6. Terminated State-
- This is the last state in the life cycle of a transaction.
- After entering the committed state or aborted state, the transaction finally enters into a terminated state where its life cycle finally comes to an end.
Next Article- ACID Properties of Transaction
Get more notes and other study material of Database Management System (DBMS).
Watch video lectures by visiting our YouTube channel LearnVidFun.