Cache Memory-
- Cache memory is a Random Access Memory.
- The main advantage of cache memory is its very fast speed.
- It can be accessed by the CPU at much faster speed than main memory.
Location-
- Cache memory lies on the path between the CPU and the main memory.
- It facilitates the transfer of data between the processor and the main memory at the speed which matches to the speed of the processor.
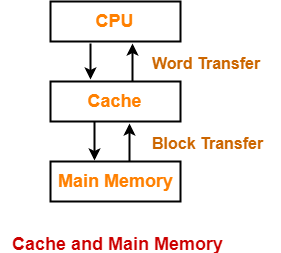
- Data is transferred in the form of words between the cache memory and the CPU.
- Data is transferred in the form of blocks or pages between the cache memory and the main memory.
Purpose-
- The fast speed of the cache memory makes it extremely useful.
- It is used for bridging the speed mismatch between the fastest CPU and the main memory.
- It does not let the CPU performance suffer due to the slower speed of the main memory.
Execution Of Program-
- Whenever any program has to be executed, it is first loaded in the main memory.
- The portion of the program that is mostly probably going to be executed in the near future is kept in the cache memory.
- This allows CPU to access the most probable portion at a faster speed.
Step-01:
Whenever CPU requires any word of memory, it is first searched in the CPU registers.
Now, there are two cases possible-
Case-01:
- If the required word is found in the CPU registers, it is read from there.
Case-02:
- If the required word is not found in the CPU registers, Step-02 is followed.
Step-02:
- When the required word is not found in the CPU registers, it is searched in the cache memory.
- Tag directory of the cache memory is used to search whether the required word is present in the cache memory or not.
Now, there are two cases possible-
Case-01:
- If the required word is found in the cache memory, the word is delivered to the CPU.
- This is known as Cache hit.
Case-02:
- If the required word is not found in the cache memory, Step-03 is followed.
- This is known as Cache miss.
Step-03:
- When the required word is not found in the cache memory, it is searched in the main memory.
- Page Table is used to determine whether the required page is present in the main memory or not.
Now, there are two cases possible-
Case-01:
If the page containing the required word is found in the main memory,
- The page is mapped from the main memory to the cache memory.
- This mapping is performed using cache mapping techniques.
- Then, the required word is delivered to the CPU.
Case-02:
If the page containing the required word is not found in the main memory,
- A page fault occurs.
- The page containing the required word is mapped from the secondary memory to the main memory.
- Then, the page is mapped from the main memory to the cache memory.
- Then, the required word is delivered to the CPU.
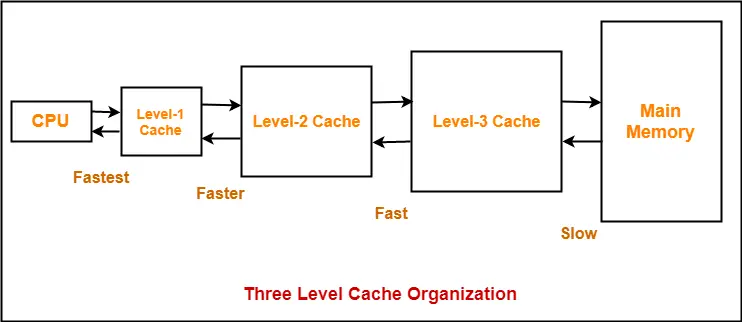
Multilevel Cache Organization-
- A multilevel cache organization is an organization where cache memories of different sizes are organized at multiple levels to increase the processing speed to a greater extent.
- The smaller the size of cache, the faster its speed.
- The smallest size cache memory is placed closest to the CPU.
- This helps to achieve better performance in terms of speed.
Example-
Three level cache organization consists of three cache memories of different size organized at three different levels as shown below-
Size (L1 Cache) < Size (L2 Cache) < Size (L3 Cache) < Size (Main Memory)
To gain better understanding about Cache Memory,
Next Article- Cache Mapping Techniques
Get more notes and other study material of Computer Organization and Architecture.
Watch video lectures by visiting our YouTube channel LearnVidFun.