Subnetting in Networking-
In networking,
- The process of dividing a single network into multiple sub networks is called as subnetting.
- The sub networks so created are called as subnets.
Example-
Following diagram shows the subnetting of a big single network into 4 smaller subnets-
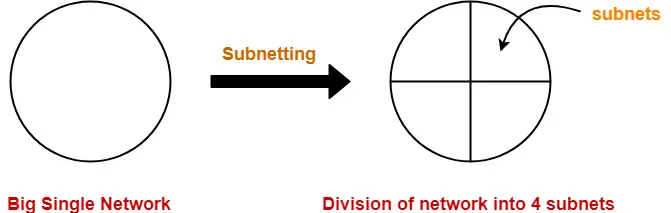
Advantages-
The two main advantages of subnetting a network are-
- It improves the security.
- The maintenance and administration of subnets is easy.
Subnet ID-
- Each subnet has its unique network address known as its Subnet ID.
- The subnet ID is created by borrowing some bits from the Host ID part of the IP Address.
- The number of bits borrowed depends on the number of subnets created.
Types of Subnetting-
Subnetting of a network may be carried out in the following two ways-

- Fixed Length Subnetting
- Variable Length Subnetting
1. Fixed Length Subnetting-
Fixed length subnetting also called as classful subnetting divides the network into subnets where-
- All the subnets are of same size.
- All the subnets have equal number of hosts.
- All the subnets have same subnet mask.
2. Variable Length Subnetting-
Variable length subnetting also called as classless subnetting divides the network into subnets where-
- All the subnets are not of same size.
- All the subnets do not have equal number of hosts.
- All the subnets do not have same subnet mask.
Subnetting Examples-
Now, we shall discuss some examples of subnetting a network-
Example-01:
Consider-
- We have a big single network having IP Address 200.1.2.0.
- We want to do subnetting and divide this network into 2 subnets.
Clearly, the given network belongs to class C.

Also Read- Classes of IP Address
For creating two subnets and to represent their subnet IDs, we require 1 bit.
So,
- We borrow one bit from the Host ID part.
- After borrowing one bit, Host ID part remains with only 7 bits.
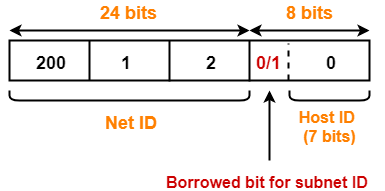
- If borrowed bit = 0, then it represents the first subnet.
- If borrowed bit = 1, then it represents the second subnet.
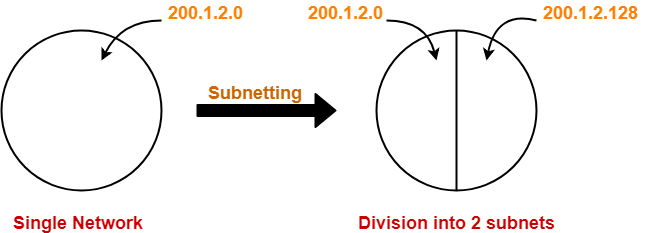
IP Address of the two subnets are-
- 200.1.2.00000000 = 200.1.2.0
- 200.1.2.10000000 = 200.1.2.128
For 1st Subnet-
- IP Address of the subnet = 200.1.2.0
- Total number of IP Addresses = 27 = 128
- Total number of hosts that can be configured = 128 – 2 = 126
- Range of IP Addresses = [200.1.2.00000000, 200.1.2.01111111] = [200.1.2.0, 200.1.2.127]
- Direct Broadcast Address = 200.1.2.01111111 = 200.1.2.127
- Limited Broadcast Address = 255.255.255.255
For 2nd Subnet-
- IP Address of the subnet = 200.1.2.128
- Total number of IP Addresses = 27 = 128
- Total number of hosts that can be configured = 128 – 2 = 126
- Range of IP Addresses = [200.1.2.10000000, 200.1.2.11111111] = [200.1.2.128, 200.1.2.255]
- Direct Broadcast Address = 200.1.2.11111111 = 200.1.2.255
- Limited Broadcast Address = 255.255.255.255
Example-02:
Consider-
- We have a big single network having IP Address 200.1.2.0.
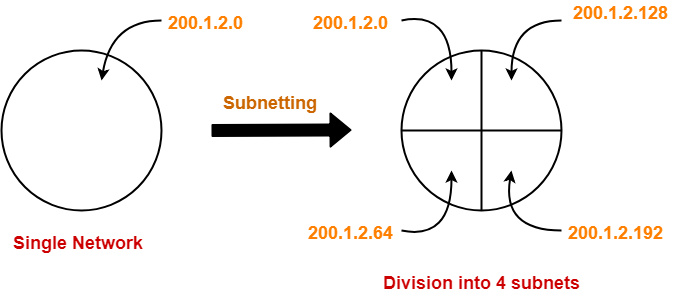
- We want to do subnetting and divide this network into 4 subnets.
Clearly, the given network belongs to class C.
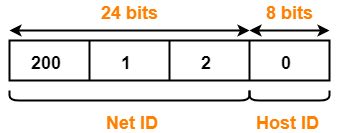
For creating four subnets and to represent their subnet IDs, we require 2 bits.
So,
- We borrow two bits from the Host ID part.
- After borrowing two bits, Host ID part remains with only 6 bits.
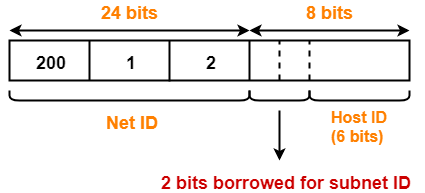
- If borrowed bits = 00, then it represents the 1st subnet.
- If borrowed bits = 01, then it represents the 2nd subnet.
- If borrowed bits = 10, then it represents the 3rd subnet.
- If borrowed bits = 11, then it represents the 4th subnet.
IP Address of the four subnets are-
- 200.1.2.00000000 = 200.1.2.0
- 200.1.2.01000000 = 200.1.2.64
- 200.1.2.10000000 = 200.1.2.128
- 200.1.2.11000000 = 200.1.2.192
For 1st Subnet-
- IP Address of the subnet = 200.1.2.0
- Total number of IP Addresses = 26 = 64
- Total number of hosts that can be configured = 64 – 2 = 62
- Range of IP Addresses = [200.1.2.00000000, 200.1.2.00111111] = [200.1.2.0, 200.1.2.63]
- Direct Broadcast Address = 200.1.2.00111111 = 200.1.2.63
- Limited Broadcast Address = 255.255.255.255
For 2nd Subnet-
- IP Address of the subnet = 200.1.2.64
- Total number of IP Addresses = 26 = 64
- Total number of hosts that can be configured = 64 – 2 = 62
- Range of IP Addresses = [200.1.2.01000000, 200.1.2.01111111] = [200.1.2.64, 200.1.2.127]
- Direct Broadcast Address = 200.1.2.01111111 = 200.1.2.127
- Limited Broadcast Address = 255.255.255.255
For 3rd Subnet-
- IP Address of the subnet = 200.1.2.128
- Total number of IP Addresses = 26 = 64
- Total number of hosts that can be configured = 64 – 2 = 62
- Range of IP Addresses = [200.1.2.10000000, 200.1.2.10111111] = [200.1.2.128, 200.1.2.191]
- Direct Broadcast Address = 200.1.2.10111111 = 200.1.2.191
- Limited Broadcast Address = 255.255.255.255
For 4th Subnet-
- IP Address of the subnet = 200.1.2.192
- Total number of IP Addresses = 26 = 64
- Total number of hosts that can be configured = 64 – 2 = 62
- Range of IP Addresses = [200.1.2.11000000, 200.1.2.11111111] = [200.1.2.192, 200.1.2.255]
- Direct Broadcast Address = 200.1.2.11111111 = 200.1.2.255
- Limited Broadcast Address = 255.255.255.255
Example-03:
Consider-
- We have a big single network having IP Address 200.1.2.0.
- We want to do subnetting and divide this network into 3 subnets.
Here, the subnetting will be performed in two steps-
- Dividing the given network into 2 subnets
- Dividing one of the subnets further into 2 subnets
Step-01: Dividing Given Network into 2 Subnets-
The subnetting will be performed exactly in the same way as performed in Example-01.
After subnetting, we have-

Step-02: Dividing One Subnet into 2 Subnets-
- We perform the subnetting of one of the subnets further into 2 subnets.
- Consider we want to do subnetting of the 2nd subnet having IP Address 200.1.2.128.
For creating two subnets and to represent their subnet IDs, we require 1 bit.
So,
- We borrow one more bit from the Host ID part.
- After borrowing one bit, Host ID part remains with only 6 bits.
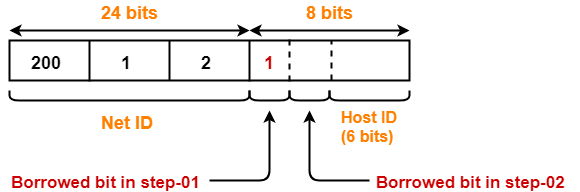
- If 2nd borrowed bit = 0, then it represents one subnet.
- If 2nd borrowed bit = 1, then it represents the other subnet.
IP Address of the two subnets are-
- 200.1.2.10000000 = 200.1.2.128
- 200.1.2.11000000 = 200.1.2.192
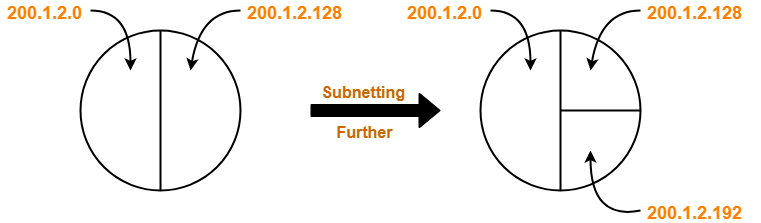
Finally, the given single network is divided into 3 subnets having IP Address-
- 200.1.2.0
- 200.1.2.128
- 200.1.2.192
For 1st Subnet-
- IP Address of the subnet = 200.1.2.0
- Total number of IP Addresses = 27 = 128
- Total number of hosts that can be configured = 128 – 2 = 126
- Range of IP Addresses = [200.1.2.00000000, 200.1.2.01111111] = [200.1.2.0, 200.1.2.127]
- Direct Broadcast Address = 200.1.2.01111111 = 200.1.2.127
- Limited Broadcast Address = 255.255.255.255
For 2nd Subnet-
- IP Address of the subnet = 200.1.2.128
- Total number of IP Addresses = 26 = 64
- Total number of hosts that can be configured = 64 – 2 = 62
- Range of IP Addresses = [200.1.2.10000000, 200.1.2.10111111] = [200.1.2.128, 200.1.2.191]
- Direct Broadcast Address = 200.1.2.10111111 = 200.1.2.191
- Limited Broadcast Address = 255.255.255.255
For 3rd Subnet-
- IP Address of the subnet = 200.1.2.192
- Total number of IP Addresses = 26 = 64
- Total number of hosts that can be configured = 64 – 2 = 62
- Range of IP Addresses = [200.1.2.11000000, 200.1.2.11111111] = [200.1.2.192, 200.1.2.255]
- Direct Broadcast Address = 200.1.2.11111111 = 200.1.2.255
- Limited Broadcast Address = 255.255.255.255
Disadvantages of Subnetting-
Point-01:
| Subnetting leads to loss of IP Addresses. |
During subnetting,
- We have to face a loss of IP Addresses.
- This is because two IP Addresses are wasted for each subnet.
- One IP address is wasted for its network address.
- Other IP Address is wasted for its direct broadcasting address.
Point-02:
| Subnetting leads to complicated communication process. |
After subnetting, the communication process becomes complex involving the following 4 steps-
- Identifying the network
- Identifying the sub network
- Identifying the host
- Identifying the process
PRACTICE PROBLEMS BASED ON SUBNETTING IN NETWORKING-
Problem-01:
Suppose a network with IP Address 192.16.0.0. is divided into 2 subnets, find number of hosts per subnet.
Also for the first subnet, find-
- Subnet Address
- First Host ID
- Last Host ID
- Broadcast Address
Solution-
- Given IP Address belongs to class C.
- So, 24 bits are reserved for the Net ID.
- The given network is divided into 2 subnets.
- So, 1 bit is borrowed from the host ID part for the subnet IDs.
- Then, Number of bits remaining for the Host ID = 7.
- Thus, Number of hosts per subnet = 27 = 128.
For 1st Subnet-
- Subnet Address = First IP Address = 192.16.0.00000000 = 172.16.0.0
- First Host ID = 192.16.0.00000001 = 192.16.0.1
- Last Host ID = 192.16.0.01111110 = 192.16.0.126
- Broadcast Address = Last IP Address = 192.16.0.01111111 = 172.16.0.127
Problem-02:
What is not true about subnetting?
- It is applied for a single network
- It is used to improve security
- Bits are borrowed from network portion
- Bits are borrowed from Host portion
Solution-
Clearly, Option (C) is correct.
Problem-03:
In a class B, network on the internet has a subnet mask of 255.255.240.0. What is the maximum number of hosts per subnet?
- 4096
- 4094
- 4092
- 4090
Solution-
- Number of bits reserved for network ID in the given subnet mask = 20.
- So, Number of bits reserved for Host ID = 32 – 20 = 12 bits.
- Thus, Number of hosts per subnet = 212 – 2 = 4094.
- In class B, 16 bits are reserved for the network.
- So, Number of bits reserved for subnet ID = 20 – 16 = 4 bits.
- Number of subnets possible = 24 = 16.
- Thus, Option (B) is correct.
To gain better understanding about IPv4 Subnetting,
Next Article- Subnet Mask | Calculating Subnet Mask
Get more notes and other study material of Computer Networks.
Watch video lectures by visiting our YouTube channel LearnVidFun.

