Semaphore in OS-
Before you go through this article, make sure that you have gone through the previous article on Semaphores in OS.
We have discussed-
- A semaphore is a simple integer variable used to provide synchronization among the processes.
- There are mainly two types of semaphores-
In this article, we will discuss practice problems based on counting semaphores.
PRACTICE PROBLEMS BASED ON COUNTING SEMAPHORES IN OS-
Problem-01:
A counting semaphore S is initialized to 10. Then, 6 P operations and 4 V operations are performed on S. What is the final value of S?
Solution-
We know-
- P operation also called as wait operation decrements the value of semaphore variable by 1.
- V operation also called as signal operation increments the value of semaphore variable by 1.
Thus,
Final value of semaphore variable S
= 10 – (6 x 1) + (4 x 1)
= 10 – 6 + 4
= 8
Problem-02:
A counting semaphore S is initialized to 7. Then, 20 P operations and 15 V operations are performed on S. What is the final value of S?
Solution-
We know-
- P operation also called as wait operation decrements the value of semaphore variable by 1.
- V operation also called as signal operation increments the value of semaphore variable by 1.
Thus,
Final value of semaphore variable S
= 7 – (20 x 1) + (15 x 1)
= 7 – 20 + 15
= 2
Problem-03:
A shared variable x, initialized to zero, is operated on by four concurrent processes W, X, Y, Z as follows. Each of the processes W and X reads x from memory, increments by one, stores it to memory and then terminates. Each of the processes Y and Z reads x from memory, decrements by two, stores it to memory, and then terminates. Each process before reading x invokes the P operation (i.e. wait) on a counting semaphore S and invokes the V operation (i.e. signal) on the semaphore S after storing x to memory. Semaphore S is initialized to two. What is the maximum possible value of x after all processes complete execution?
- -2
- -1
- 1
- 2
Solution-
The given question may be pictorially represented as-
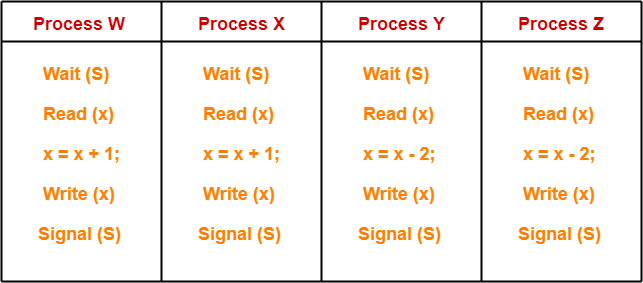
Initially, counting semaphore S is initialized with value 2.
Now, We have been asked the maximum possible value of x after all the processes complete execution.
Clearly,
- Processes W and X increments the value of x.
- Processes Y and Z decrements the value of x.
To obtain the maximum value of x, the processes must execute in such a way that-
- Only the impact of the processes W and X remains on the value of x.
- The impact of processes Y and Z gets lost on the value of x.
STRATEGY
|
This is achieved as-
Step-01:
- Process W arrives.
- It executes the wait(S) operation and the value of S decrements by 1. Now, S = 1.
- It reads the value x = 0.
- It gets preempted.
Step-02:
- Process Y arrives.
- It executes the wait(S) operation and the value of S decrements by 1. Now, S = 0.
- It reads the value x = 0.
- It decrements the value of x by 2. Now, x = 0 – 2 = -2.
- It writes the value x = -2 in the memory.
- It executes the signal(S) operation and the value of S increments by 1. Now, S = 1.
- Now, execution of process Y is completed.
Step-03:
- Process Z arrives.
- It executes the wait(S) operation and the value of S decrements by 1. Now, S = 0.
- It reads the value x = -2.
- It decrements the value of x by 2. Now, x = – 2 – 2 = -4.
- It writes the value x = -4 in the memory.
- It executes the signal(S) operation and the value of S increments by 1. Now, S = 1.
- Now, execution of process Z is completed.
Step-04:
- Process W gets scheduled again.
- It resumes its execution from where it left.
- Before preemption it had already read the value x = 0.
- Now, it increments the value of x by 1. Now, x = 0 + 1 = 1.
- It writes the value x = 1 in the memory.
- It executes the signal(S) operation and the value of S increments by 1. Now, S = 2.
- Now, execution of process W is completed.
Step-05:
- Process X arrives.
- It executes the wait(S) operation and the value of S decrements by 1. Now, S = 1.
- It reads the value x = 1.
- It increments the value of x by 1. Now, x = 1 + 1 = 2.
- It writes the value x = 2 in the memory.
- It executes the signal(S) operation and the value of S increments by 1. Now, S = 2.
- Now, execution of process X is completed.
Thus,
- Final value of x = 2.
- This is the maximum possible value of x that can be achieved after executing all the 4 processes.
- Option (D) is correct.
Problem-04:
In problem-03, what is the minimum possible value of x after all processes complete execution?
- -4
- -2
- 2
- 4
Solution-
To obtain the minimum value of x, the processes must execute in such a way that-
- Only the impact of the processes Y and Z remains on the value of x.
- The impact of processes W and X gets lost on the value of x.
This can be achieved if processes execute in the following manner-
Step-01:
- Process Y arrives.
- It executes the wait(S) operation and the value of S decrements by 1. Now, S = 1.
- It reads the value x = 0.
- It gets preempted.
Step-02:
- Process W arrives.
- It executes the wait(S) operation and the value of S decrements by 1. Now, S = 0.
- It reads the value x = 0.
- It increments the value of x by 1. Now, x = 0 + 1 = 1.
- It writes the value x = 1 in the memory.
- It executes the signal(S) operation and the value of S increments by 1. Now, S = 1.
- Now, execution of process W is completed.
Step-03:
- Process X arrives.
- It executes the wait(S) operation and the value of S decrements by 1. Now, S = 0.
- It reads the value x = 1.
- It increments the value of x by 1. Now, x = 1 + 1 = 2.
- It writes the value x = 2 in the memory.
- It executes the signal(S) operation and the value of S increments by 1. Now, S = 1.
- Now, execution of process X is completed.
Step-04:
- Process Y gets scheduled again.
- It resumes its execution from where it left.
- Before preemption it had already read the value x = 0.
- Now, it decrements the value of x by 2. Now, x = 0 – 2 = -2.
- It writes the value x = -2 in the memory.
- It executes the signal(S) operation and the value of S increments by 1. Now, S = 2.
- Now, execution of process Y is completed.
Step-05:
- Process Z arrives.
- It executes the wait(S) operation and the value of S decrements by 1. Now, S = 1.
- It reads the value x = -2.
- It decrements the value of x by 2. Now, x = -2 – 2 = -4.
- It writes the value x = -4 in the memory.
- It executes the signal(S) operation and the value of S increments by 1. Now, S = 2.
- Now, execution of process Z is completed.
Thus,
- Final value of x = -4.
- This is the minimum possible value of x that can be achieved after executing all the 4 processes.
Thus, Option (A) is correct.
To watch video solutions and practice other problems,
Next Article- Binary Semaphores
Get more notes and other study material of Operating System.
Watch video lectures by visiting our YouTube channel LearnVidFun.

