Non-Contiguous Memory Allocation-
Before you go through this article, make sure that you have gone through the previous article on Non-Contiguous Memory Allocation.
We have discussed-
- Non-contiguous memory allocation is a memory allocation technique.
- It allows to store parts of a single process in a non-contiguous fashion.
Techniques-
There are two popular techniques used for non-contiguous memory allocation-
In this article, we will discuss about Segmentation.
Segmentation-
- Like Paging, Segmentation is another non-contiguous memory allocation technique.
- In segmentation, process is not divided blindly into fixed size pages.
- Rather, the process is divided into modules for better visualization.
Characteristics-
- Segmentation is a variable size partitioning scheme.
- In segmentation, secondary memory and main memory are divided into partitions of unequal size.
- The size of partitions depend on the length of modules.
- The partitions of secondary memory are called as segments.
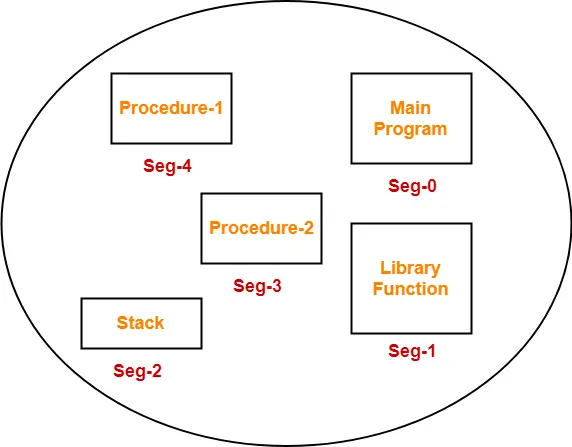
Example-
Consider a program is divided into 5 segments as-
Segment Table-
- Segment table is a table that stores the information about each segment of the process.
- It has two columns.
- First column stores the size or length of the segment.
- Second column stores the base address or starting address of the segment in the main memory.
- Segment table is stored as a separate segment in the main memory.
- Segment table base register (STBR) stores the base address of the segment table.
For the above illustration, consider the segment table is-
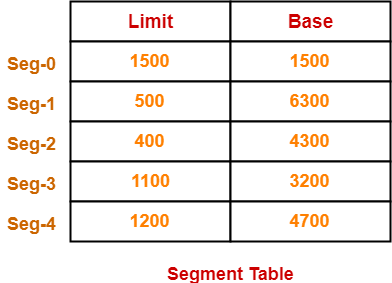
Here,
- Limit indicates the length or size of the segment.
- Base indicates the base address or starting address of the segment in the main memory.
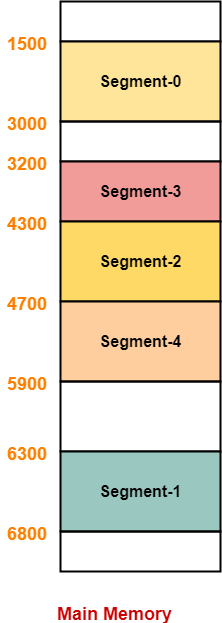
In accordance to the above segment table, the segments are stored in the main memory as-
Translating Logical Address into Physical Address-
- CPU always generates a logical address.
- A physical address is needed to access the main memory.
Following steps are followed to translate logical address into physical address-
Step-01:
CPU generates a logical address consisting of two parts-
- Segment Number
- Segment Offset
- Segment Number specifies the specific segment of the process from which CPU wants to read the data.
- Segment Offset specifies the specific word in the segment that CPU wants to read.
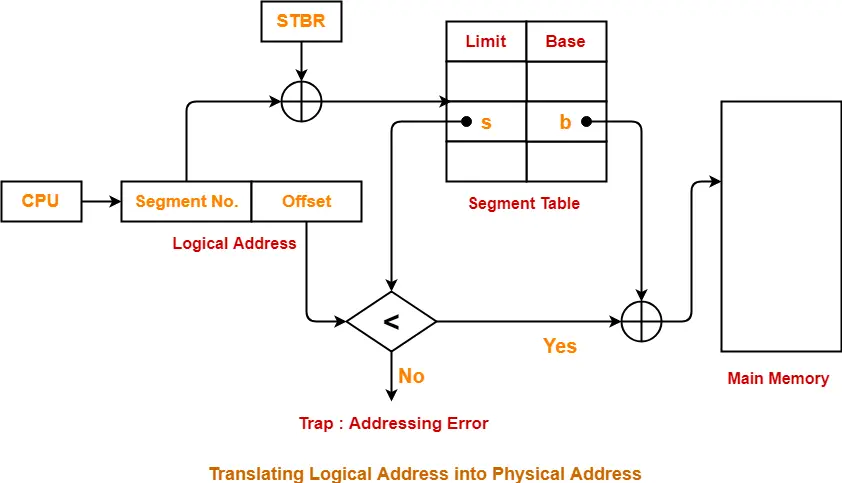
Step-02:
- For the generated segment number, corresponding entry is located in the segment table.
- Then, segment offset is compared with the limit (size) of the segment.
Now, two cases are possible-
Case-01: Segment Offset >= Limit
- If segment offset is found to be greater than or equal to the limit, a trap is generated.
Case-02: Segment Offset < Limit
- If segment offset is found to be smaller than the limit, then request is treated as a valid request.
- The segment offset must always lie in the range [0, limit-1],
- Then, segment offset is added with the base address of the segment.
- The result obtained after addition is the address of the memory location storing the required word.
Diagram-
The following diagram illustrates the above steps of translating logical address into physical address-
Advantages-
The advantages of segmentation are-
- It allows to divide the program into modules which provides better visualization.
- Segment table consumes less space as compared to Page Table in paging.
- It solves the problem of internal fragmentation.
Disadvantages-
The disadvantages of segmentation are-
- There is an overhead of maintaining a segment table for each process.
- The time taken to fetch the instruction increases since now two memory accesses are required.
- Segments of unequal size are not suited for swapping.
- It suffers from external fragmentation as the free space gets broken down into smaller pieces with the processes being loaded and removed from the main memory.
To gain better understanding about Segmentation,
Next Article- Practice Problems On Segmentation
Get more notes and other study material of Operating System.
Watch video lectures by visiting our YouTube channel LearnVidFun.

