Process Synchronization-
When multiple processes execute concurrently sharing system resources, then inconsistent results might be produced.
- Process Synchronization is a mechanism that deals with the synchronization of processes.
- It controls the execution of processes running concurrently to ensure that consistent results are produced.
Need of Synchronization-
Process synchronization is needed-
- When multiple processes execute concurrently sharing some system resources.
- To avoid the inconsistent results.
Critical Section-
Critical section is a section of the program where a process access the shared resources during its execution.
Example-
The following illustration shows how inconsistent results may be produced if multiple processes execute concurrently without any synchronization.
Consider-
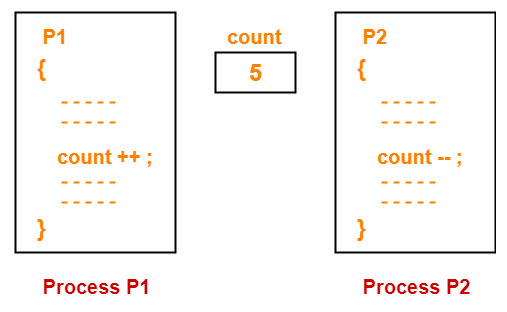
- Two processes P1 and P2 are executing concurrently.
- Both the processes share a common variable named “count” having initial value = 5.
- Process P1 tries to increment the value of count.
- Process P2 tries to decrement the value of count.
In assembly language, the instructions of the processes may be written as-
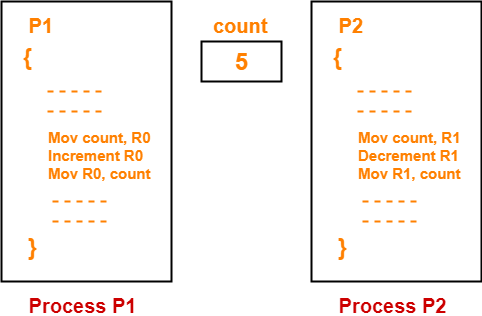
Now, when these processes execute concurrently without synchronization, different results may be produced.
Case-01:
The execution order of the instructions may be-
P1(1), P1(2), P1(3), P2(1), P2(2), P2(3)
In this case,
Final value of count = 5
Case-02:
The execution order of the instructions may be-
P2(1), P2(2), P2(3), P1(1), P1(2), P1(3)
In this case,
Final value of count = 5
Case-03:
The execution order of the instructions may be-
P1(1), P2(1), P2(2), P2(3), P1(2), P1(3)
In this case,
Final value of count = 6
Case-04:
The execution order of the instructions may be-
P2(1), P1(1), P1(2), P1(3), P2(2), P2(3)
In this case,
Final value of count = 4
Case-05:
The execution order of the instructions may be-
P1(1), P1(2), P2(1), P2(2), P1(3), P2(3)
In this case,
Final value of count = 4
It is clear from here that inconsistent results may be produced if multiple processes execute concurrently without any synchronization.
Race Condition-
Race condition is a situation where-
- The final output produced depends on the execution order of instructions of different processes.
- Several processes compete with each other.
The above example is a good illustration of race condition.
PRACTICE PROBLEM BASED ON PROCESS SYNCHRONIZATION-
Problem-
The following two functions P1 and P2 that share a variable B with an initial value of 2 execute concurrently-
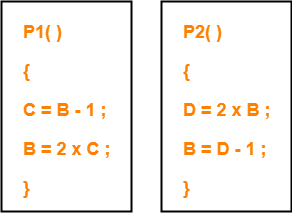
The number of distinct values that B can possibly take after the execution is-
- 3
- 2
- 5
- 4
Solution-
Different execution order of the instructions of P1 and P2 produce different results.
Case-01:
The execution order of the instructions may be-
P1(1), P1(2), P2(1), P2(2)
In this case,
Final value of B = 3
Case-02:
The execution order of the instructions may be-
P2(1), P2(2), P1(1), P1(2)
In this case,
Final value of B = 4
Case-03:
The execution order of the instructions may be-
P1(1), P2(1), P2(2), P1(2)
In this case,
Final value of B = 2
Case-04:
The execution order of the instructions may be-
P2(1), P1(1), P1(2), P2(2)
In this case,
Final value of B = 3
Case-05:
The execution order of the instructions may be-
P1(1), P2(1), P1(2), P2(2)
In this case,
Final value of B = 3
Case-06:
The execution order of the instructions may be-
P2(1), P1(1), P2(2), P1(2)
In this case,
Final value of B = 2
From here,
- Distinct values that may be produced are 2, 3 and 4.
- Number of distinct values that may be produced = 3
Thus, Option (A) is correct.
To gain better understanding of Process Synchronization,
Next Article- Synchronization Mechanisms
Get more notes and other study material of Operating System.
Watch video lectures by visiting our YouTube channel LearnVidFun.

