Introduction-
- A program consists of several number of instructions.
- These instructions may be executed in the following two ways-

- Non-Pipelined Execution
- Pipelined Execution
1. Non-Pipelined Execution-
In non-pipelined architecture,
- All the instructions of a program are executed sequentially one after the other.
- A new instruction executes only after the previous instruction has executed completely.
- This style of executing the instructions is highly inefficient.
Example-
Consider a program consisting of three instructions.
In a non-pipelined architecture, these instructions execute one after the other as-
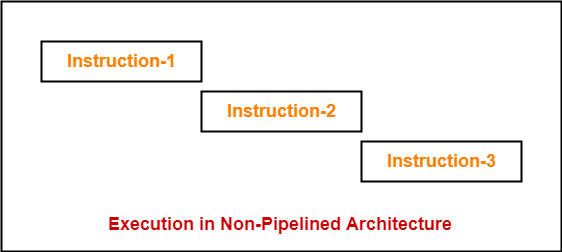
If time taken for executing one instruction = t, then-
Time taken for executing ‘n’ instructions = n x t
2. Pipelined Execution-
In pipelined architecture,
- Multiple instructions are executed parallely.
- This style of executing the instructions is highly efficient.
Now, let us discuss instruction pipelining in detail.
Instruction Pipelining-
| Instruction pipelining is a technique that implements a form of parallelism called as instruction level parallelism within a single processor. |
- A pipelined processor does not wait until the previous instruction has executed completely.
- Rather, it fetches the next instruction and begins its execution.
Pipelined Architecture-
In pipelined architecture,
- The hardware of the CPU is split up into several functional units.
- Each functional unit performs a dedicated task.
- The number of functional units may vary from processor to processor.
- These functional units are called as stages of the pipeline.
- Control unit manages all the stages using control signals.
- There is a register associated with each stage that holds the data.
- There is a global clock that synchronizes the working of all the stages.
- At the beginning of each clock cycle, each stage takes the input from its register.
- Each stage then processes the data and feed its output to the register of the next stage.
Four-Stage Pipeline-
In four stage pipelined architecture, the execution of each instruction is completed in following 4 stages-
- Instruction fetch (IF)
- Instruction decode (ID)
- Instruction Execute (IE)
- Write back (WB)
To implement four stage pipeline,
- The hardware of the CPU is divided into four functional units.
- Each functional unit performs a dedicated task.
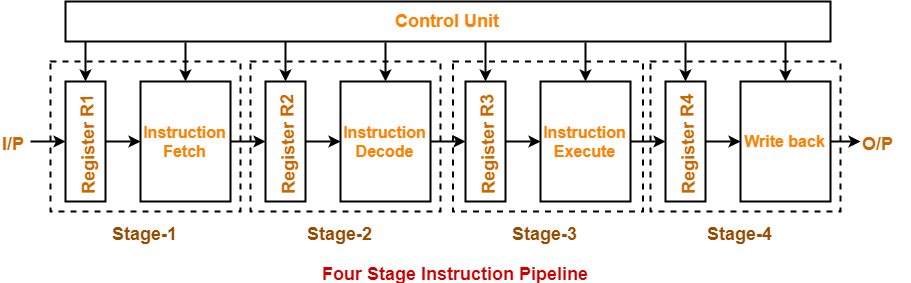
Stage-01:
At stage-01,
- First functional unit performs instruction fetch.
- It fetches the instruction to be executed.
Stage-02:
At stage-02,
- Second functional unit performs instruction decode.
- It decodes the instruction to be executed.
Stage-03:
At stage-03,
- Third functional unit performs instruction execution.
- It executes the instruction.
Stage-04:
At stage-04,
- Fourth functional unit performs write back.
- It writes back the result so obtained after executing the instruction.
Execution-
In pipelined architecture,
- Instructions of the program execute parallely.
- When one instruction goes from nth stage to (n+1)th stage, another instruction goes from (n-1)th stage to nth stage.
Phase-Time Diagram-
- Phase-time diagram shows the execution of instructions in the pipelined architecture.
- The following diagram shows the execution of three instructions in four stage pipeline architecture.
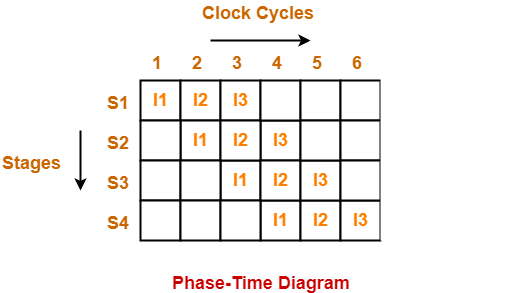
Time taken to execute three instructions in four stage pipelined architecture = 6 clock cycles.
NOTE-
In non-pipelined architecture,
Time taken to execute three instructions would be
= 3 x Time taken to execute one instruction
= 3 x 4 clock cycles
= 12 clock cycles
Clearly, pipelined execution of instructions is far more efficient than non-pipelined execution.
To gain better understanding about Pipelining in Computer Architecture,
Next Article- Instruction Pipeline | Formulas
Get more notes and other study material of Computer Organization and Architecture.
Watch video lectures by visiting our YouTube channel LearnVidFun.

