Non-Contiguous Memory Allocation-
- Non-contiguous memory allocation is a memory allocation technique.
- It allows to store parts of a single process in a non-contiguous fashion.
- Thus, different parts of the same process can be stored at different places in the main memory.
Techniques-
There are two popular techniques used for non-contiguous memory allocation-
- Paging
- Segmentation
In this article, we will discuss about Paging.
Learn about Segmentation.
Paging-
- Paging is a fixed size partitioning scheme.
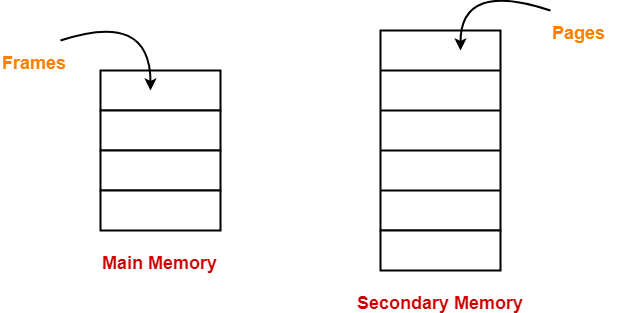
- In paging, secondary memory and main memory are divided into equal fixed size partitions.
- The partitions of secondary memory are called as pages.
- The partitions of main memory are called as frames.
- Each process is divided into parts where size of each part is same as page size.
- The size of the last part may be less than the page size.
- The pages of process are stored in the frames of main memory depending upon their availability.
Example-
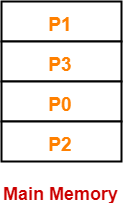
- Consider a process is divided into 4 pages P0, P1, P2 and P3.
- Depending upon the availability, these pages may be stored in the main memory frames in a non-contiguous fashion as shown-
Also Read- Contiguous Memory Allocation
Translating Logical Address into Physical Address-
- CPU always generates a logical address.
- A physical address is needed to access the main memory.
Following steps are followed to translate logical address into physical address-
Step-01:
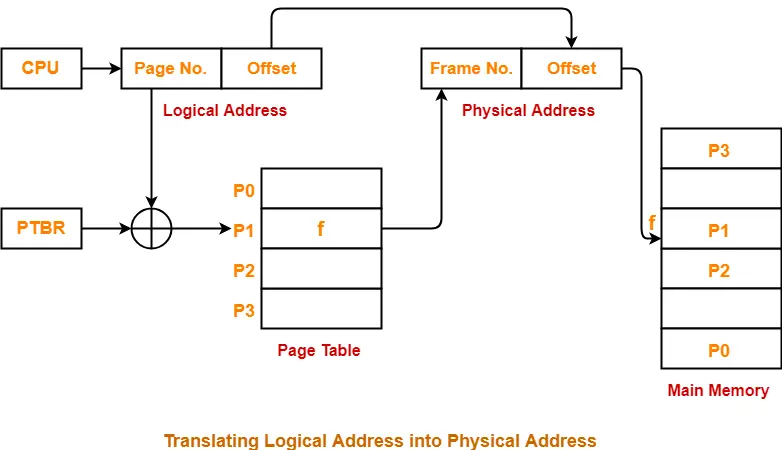
CPU generates a logical address consisting of two parts-
- Page Number
- Page Offset
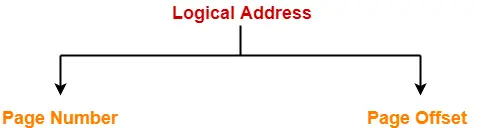
- Page Number specifies the specific page of the process from which CPU wants to read the data.
- Page Offset specifies the specific word on the page that CPU wants to read.
Step-02:
For the page number generated by the CPU,
- Page Table provides the corresponding frame number (base address of the frame) where that page is stored in the main memory.
Step-03:
- The frame number combined with the page offset forms the required physical address.
- Frame number specifies the specific frame where the required page is stored.
- Page Offset specifies the specific word that has to be read from that page.
Diagram-
The following diagram illustrates the above steps of translating logical address into physical address-
Advantages-
The advantages of paging are-
- It allows to store parts of a single process in a non-contiguous fashion.
- It solves the problem of external fragmentation.
Disadvantages-
The disadvantages of paging are-
- It suffers from internal fragmentation.
- There is an overhead of maintaining a page table for each process.
- The time taken to fetch the instruction increases since now two memory accesses are required.
To gain better understanding about Paging,
Next Article- Page Table | Page Table Entry
Get more notes and other study material of Operating System.
Watch video lectures by visiting our YouTube channel LearnVidFun.

