Paging in OS-
Before you go through this article, make sure that you have gone through the previous articles on Paging in OS.
We have discussed-
- Paging is a non-contiguous memory allocation technique.
- Page Table is a table that maps a page number to the frame number containing that page.
- Multilevel Paging is a paging scheme where there exists a hierarchy of page tables.
Also Read- Important Formulas of Paging
In this article, we will discuss practice problems based on multilevel paging.
PRACTICE PROBLEMS BASED ON MULTILEVEL PAGING IN OS-
Problem-01:
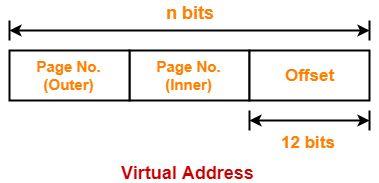
Consider a single level paging scheme. The page size is 4 KB and page table entry size is 4 bytes. The size of page table is 4 KB. Give the division of virtual address space.
Solution-
Given-
- Page size = 4 KB
- Page table entry size = 4 bytes
- Page table size = 4 KB
Let the number of bits in virtual address = n bits
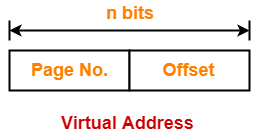
Number of Bits in Page Offset-
We have,
Page size
= 4 KB
= 212 B
Thus, Number of bits in page offset = 12 bits
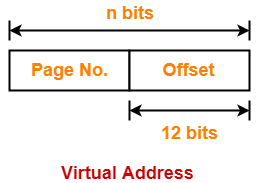
Process Size-
Number of bits in virtual address = n bits
Thus,
Process size = 2n bytes
Number of Pages of Process-
Number of pages the process is divided
= Process size / Page size
= 2n B / 4 KB
= 2n B / 212 B
= 2n-12 pages
Page Table Size-
Page table keeps track of the frames storing the pages of process.
Page table size
= Number of entries in page table x Page table entry size
= Number of pages the process is divided x Page table entry size
= 2n-12 x 4 bytes
= 2n-12+2 bytes
= 2n-10 bytes
But we are given page table size = 4 KB
Thus,
2n-10 bytes = 4 KB
2n-10 = 212
n – 10 = 12
∴ n = 22
Thus, number of bits in virtual address = 22 bits
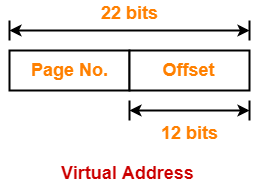
Number of Bits Required to Search an Entry in Page Table-
Method-01:
Number of bits required to search a particular entry in page table
= Number of bits in virtual address – Number of bits in page offset
= 22 bits – 12 bits
= 10 bits
Method-02:
Number of entries in page table
= Number of pages the process is divided
= 2n-12
= 222-12
= 210
Thus, Number of bits required to search a particular entry in page table = 10 bits
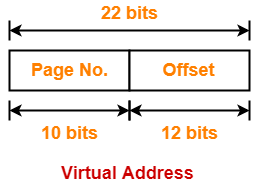
Problem-02:
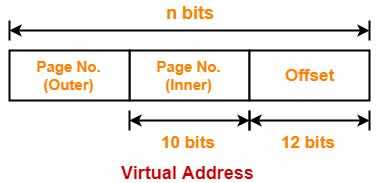
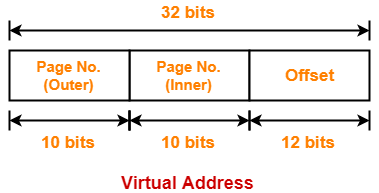
Consider a two level paging scheme. The page size is 4 KB and page table entry size is 4 bytes. The size of outer page table is 4 KB. Give the division of virtual address space.
Solution-
Given-
- Page size = 4 KB
- Page table entry size = 4 bytes
- Page table size = 4 KB
Let the number of bits in virtual address = n bits

Number of Bits in Page Offset-
We have,
Page size
= 4 KB
= 212 B
Thus, Number of bits in page offset = 12 bits
Process Size-
Number of bits in virtual address = n bits
Thus,
Process size = 2n bytes
Number of Pages of Process-
Number of pages the process is divided
= Process size / Page size
= 2n B / 4 KB
= 2n B / 212 B
= 2n-12 pages
Inner Page Table Size-
Inner page table keeps track of the frames storing the pages of process.
Inner page table size
= Number of entries in inner page table x Page table entry size
= Number of pages the process is divided x Page table entry size
= 2n-12 x 4 bytes
= 2n-12+2 bytes
= 2n-10 bytes
Number of Pages of Inner Page Table-
Number of pages the inner page table is divided
= Inner page table size / Page size
= 2n-10 B / 4 KB
= 2n-10 B / 212 B
= 2n-10-12
= 2n-22 pages
Now, these 2n-22 pages of inner page table are stored in different frames of the main memory.
Number of Page Table Entries in One Page of Inner Page Table-
Number of page table entries in one page of inner page table
= Page size / Page table entry size
= 4 KB / 4 bytes
= 1 K
= 210 entries
Number of Bits Required to Search an Entry in One Page of Inner Page Table-
One page of inner page table contains 210 entries.
Thus,
Number of bits required to search a particular entry in one page of inner page table = 10 bits
Outer Page Table Size-
Outer page table is required to keep track of the frames storing the pages of inner page table.
Outer page table size
= Number of entries in outer page table x Page table entry size
= Number of pages the inner page table is divided x Page table entry size
= 2n-22 x 4 bytes
= 2n-22+2 bytes
= 2n-20 bytes
But we are given outer page table size = 4 KB
Thus,
2n-20 bytes = 4 KB
2n-20 = 212
n – 20 = 12
∴ n = 32
Thus, number of bits in virtual address = 32 bits

Number of Bits Required to Search an Entry in Outer Page Table-
Method-01:
Number of bits required to search a particular entry in outer page table
= Number of bits in virtual address – (Number of bits required to search an entry in inner page table + Number of bits in page offset)
= 32 bits – (10 bits + 12 bits)
= 32 bits – 22 bits
= 10 bits
Method-02:
Number of entries in outer page table
= Number of pages the inner page table is divided
= 2n-22
= 232-22
= 210
Thus, Number of bits required to search a particular entry in outer page table = 10 bits
Problem-03:
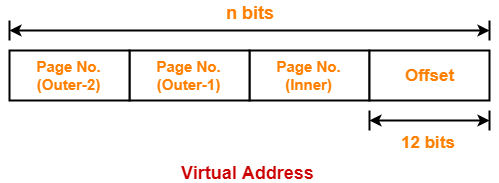
Consider a three level paging scheme. The page size is 4 KB and page table entry size is 4 bytes. The size of outermost page table is 4 KB. Give the division of virtual address space.
Solution-
Given-
- Page size = 4 KB
- Page table entry size = 4 bytes
- Page table size = 4 KB
Let the number of bits in virtual address = n bits

Number of Bits in Page Offset-
We have,
Page size
= 4 KB
= 212 B
Thus, Number of bits in page offset = 12 bits
Process Size-
Number of bits in virtual address = n bits
Thus,
Process size = 2n bytes
Number of Pages of Process-
Number of pages the process is divided
= Process size / Page size
= 2n B / 4 KB
= 2n B / 212 B
= 2n-12 pages
Inner Page Table Size-
Inner page table keeps track of the frames storing the pages of process.
Inner page table size
= Number of entries in inner page table x Page table entry size
= Number of pages the process is divided x Page table entry size
= 2n-12 x 4 bytes
= 2n-12+2 bytes
= 2n-10 bytes
Number of Pages of Inner Page Table-
Number of pages the inner page table is divided
= Inner page table size / Page size
= 2n-10 B / 4 KB
= 2n-10 B / 212 B
= 2n-10-12
= 2n-22 pages
Now, these 2n-22 pages of inner page table are stored in different frames of the main memory.
Number of Page Table Entries in One Page of Inner Page Table-
Number of page table entries in one page of inner page table
= Page size / Page table entry size
= 4 KB / 4 bytes
= 1 K
= 210 entries
Number of Bits Required to Search an Entry in One Page of Inner Page Table-
One page of inner page table contains 210 entries.
Thus,
Number of bits required to search a particular entry in one page of inner page table = 10 bits
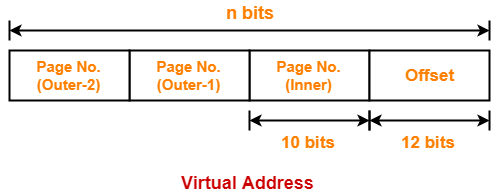
Outer Page Table-1 Size-
Outer page table-1 is required to keep track of the frames storing the pages of inner page table.
Outer page table-1 size
= Number of entries in outer page table-1 x Page table entry size
= Number of pages the inner page table is divided x Page table entry size
= 2n-22 x 4 bytes
= 2n-22+2 bytes
= 2n-20 bytes
Number of Pages of Outer Page Table-1
Number of pages the outer page table-1 is divided
= Outer page table-1 size / Page size
= 2n-20 B / 4 KB
= 2n-20 B / 212 B
= 2n-20-12
= 2n-32 pages
Now, these 2n-32 pages of outer page table-1 are stored in different frames of the main memory.
Number of Page Table Entries in One Page of Outer Page Table-1
Number of page table entries in one page of outer page table-1
= Page size / Page table entry size
= 4 KB / 4 bytes
= 1 K
= 210 entries
Number of Bits Required to Search an Entry in One Page of Outer Page Table-1
One page of outer page table-1 contains 210 entries.
Thus,
Number of bits required to search a particular entry in one page of outer page table-1 = 10 bits
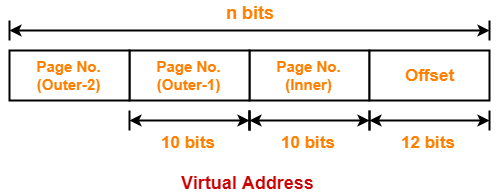
Outer Page Table-2 Size-
Outer page table-2 is required to keep track of the frames storing the pages of outer page table-1.
Outer page table-2 size
= Number of entries in outer page table-2 x Page table entry size
= Number of pages the outer page table-1 is divided x Page table entry size
= 2n-32 x 4 bytes
= 2n-32+2 bytes
= 2n-30 bytes
But we are given outermost page table size = 4 KB
Thus,
2n-30 bytes = 4 KB
2n-30 = 212
n – 30 = 12
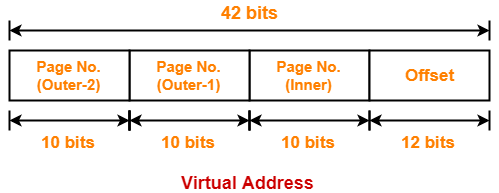
∴ n = 42
Thus, number of bits in virtual address = 42 bits
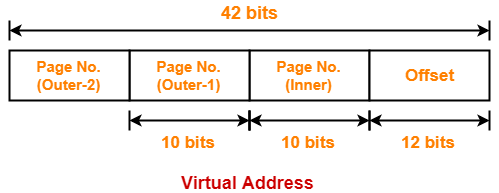
Number of Bits Required to Search an Entry in Outer Page Table-2
Method-01:
Number of bits required to search a particular entry in outer page table-2
= Number of bits in virtual address – (Number of bits required to search an entry in outer page table-1 + Number of bits required to search an entry in inner page table + Number of bits in page offset)
= 42 bits – (10 bits + 10 bits + 12 bits)
= 42 bits – 32 bits
= 10 bits
Method-02:
Number of entries in outer page table-2
= Number of pages the outer page table-1 is divided
= 2n-32
= 242-32
= 210
Thus, Number of bits required to search a particular entry in outer page table-2 = 10 bits
Problem-04:
Complete the following table-
| Page Size | Page Table Entry Size | Outermost Page Table Size | Levels of Paging | Virtual Address Space Division |
| 4 KB | 4 bytes | 256 bytes | 1 | ? |
| 4 KB | 4 bytes | 256 bytes | 2 | ? |
| 4 KB | 4 bytes | 256 bytes | 3 | ? |
Solution-
- We have to solve these problems in exactly the same manner as we have solved above.
- So, try yourself.
The answers to these problems are-
- 6 bits, 12 bits
- 6 bits, 10 bits, 12 bits
- 6 bits, 10 bits, 10 bits, 12 bits
Next Article- Practice Problems On Multilevel Paging Using TLB | Set-03
Get more notes and other study material of Operating System.
Watch video lectures by visiting our YouTube channel LearnVidFun.

