Paging in OS-
Before you go through this article, make sure that you have gone through the previous article on Paging in OS.
We have discussed-
- Paging is a non-contiguous memory allocation technique.
- In a paging scheme, a process is divided into several pages.
- The pages are then stored in different frames of the main memory.
Page Fault-
- When a page referenced by the CPU is not found in the main memory, it is called as a page fault.
- When a page fault occurs, the required page has to be fetched from the secondary memory into the main memory.
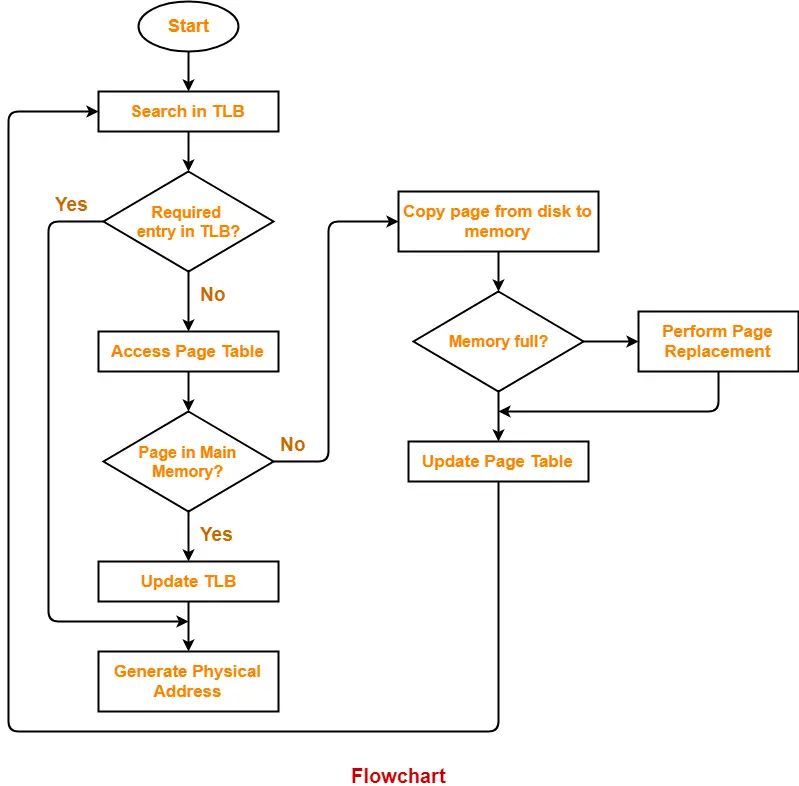
Translating Logical Address into Physical Address-
In a paging scheme using TLB with possibility of page fault,
The logical address generated by the CPU is translated into the physical address using the following steps-
Step-01:
CPU generates a logical address consisting of two parts-
- Page Number
- Page Offset
Step-02:
- TLB is checked to see if it contains an entry for the referenced page number.
- The referenced page number is compared with the TLB entries all at once.
Now, two cases are possible-
Case-01: If there is a TLB hit-
- If TLB contains an entry for the referenced page number, a TLB hit occurs.
- In this case, TLB entry is used to get the frame number for the referenced page number.
Case-02: If there is a TLB miss-
- If TLB does not contain an entry for the referenced page number, a TLB miss occurs.
- In this case, page table is used to get the frame number for the referenced page number.
- The valid / invalid bit of the page table entry indicates whether the referenced page is present in the main memory or not.
Also read- Page Table Entries
Now, two cases are possible-
Case-01: If Valid / Invalid Bit is Set to 1-
- If valid / invalid bit is set to 1, it indicates that the page is present in the main memory.
- Then, page table is used to get the frame number for the referenced page number.
- Then, TLB is updated with the page number and its frame number for future references.
Case-02: If Valid / Invalid Bit is Set to 0-
- If valid / invalid bit is set to 0, it indicates that the page is not present in the main memory.
- A page fault occurs.
- The occurrence of page fault calls the page fault interrupt which executes the page fault handling routine.
Page Fault Handling Routine-
The following sequence of events take place-
- The currently running process is stopped and context switching occurs.
- The referenced page is copied from the secondary memory to the main memory.
- If the main memory is already full, a page is replaced to create a room for the referenced page.
- After copying the referenced page successfully in the main memory, the page table is updated.
- When the execution of process is resumed, step-02 repeats.
Step-03:
- After the frame number is obtained, it is combined with the page offset to generate the physical address.
- Then, physical address is used to read the required word from the main memory.
Flowchart-
The following flowchart illustrates the above steps of translating logical address into physical address-
Page Fault Service Time-
- The time taken by the page fault handling routine to service the page fault is called as page fault service time.
- Page fault service time is much greater than main memory access time.
- It increases the effective access time.
To gain better understanding about Page Fault in OS,
Next Article- Page Replacement Algorithms
Get more notes and other study material of Operating System.
Watch video lectures by visiting our YouTube channel LearnVidFun.

