Collision Resolution Techniques-
Before you go through this article, make sure that you have gone through the previous article on Collision Resolution Techniques.
We have discussed-
- Hashing is a well-known searching technique.
- Collision occurs when hash value of the new key maps to an occupied bucket of the hash table.
- Collision resolution techniques are classified as-
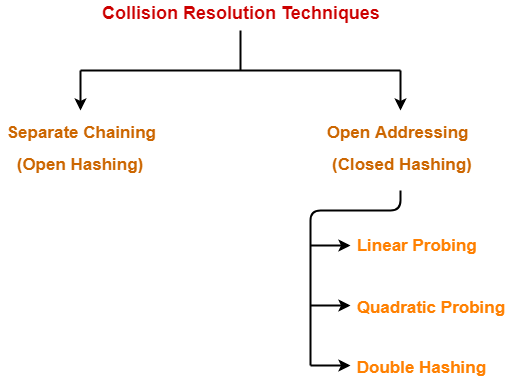
In this article, we will discuss about Open Addressing.
Open Addressing-
In open addressing,
- Unlike separate chaining, all the keys are stored inside the hash table.
- No key is stored outside the hash table.
Techniques used for open addressing are-
- Linear Probing
- Quadratic Probing
- Double Hashing
Operations in Open Addressing-
Let us discuss how operations are performed in open addressing-
Insert Operation-
- Hash function is used to compute the hash value for a key to be inserted.
- Hash value is then used as an index to store the key in the hash table.
In case of collision,
- Probing is performed until an empty bucket is found.
- Once an empty bucket is found, the key is inserted.
- Probing is performed in accordance with the technique used for open addressing.
Search Operation-
To search any particular key,
- Its hash value is obtained using the hash function used.
- Using the hash value, that bucket of the hash table is checked.
- If the required key is found, the key is searched.
- Otherwise, the subsequent buckets are checked until the required key or an empty bucket is found.
- The empty bucket indicates that the key is not present in the hash table.
Delete Operation-
- The key is first searched and then deleted.
- After deleting the key, that particular bucket is marked as “deleted”.
NOTE-
- During insertion, the buckets marked as “deleted” are treated like any other empty bucket.
- During searching, the search is not terminated on encountering the bucket marked as “deleted”.
- The search terminates only after the required key or an empty bucket is found.
Open Addressing Techniques-
Techniques used for open addressing are-
1. Linear Probing-
In linear probing,
- When collision occurs, we linearly probe for the next bucket.
- We keep probing until an empty bucket is found.
Advantage-
- It is easy to compute.
Disadvantage-
- The main problem with linear probing is clustering.
- Many consecutive elements form groups.
- Then, it takes time to search an element or to find an empty bucket.
Time Complexity-
| Worst time to search an element in linear probing is O (table size). |
This is because-
- Even if there is only one element present and all other elements are deleted.
- Then, “deleted” markers present in the hash table makes search the entire table.
2. Quadratic Probing-
In quadratic probing,
- When collision occurs, we probe for i2‘th bucket in ith iteration.
- We keep probing until an empty bucket is found.
3. Double Hashing-
In double hashing,
- We use another hash function hash2(x) and look for i * hash2(x) bucket in ith iteration.
- It requires more computation time as two hash functions need to be computed.
Comparison of Open Addressing Techniques-
Linear Probing |
Quadratic Probing |
Double Hashing |
|
Primary Clustering |
Yes | No | No |
Secondary Clustering |
Yes | Yes | No |
Number of Probe Sequence(m = size of table) |
m | m | m2 |
Cache performance |
Best | Lies between the two | Poor |
Conclusions-
- Linear Probing has the best cache performance but suffers from clustering.
- Quadratic probing lies between the two in terms of cache performance and clustering.
- Double caching has poor cache performance but no clustering.
Load Factor (α)-
Load factor (α) is defined as-

In open addressing, the value of load factor always lie between 0 and 1.
This is because-
- In open addressing, all the keys are stored inside the hash table.
- So, size of the table is always greater or at least equal to the number of keys stored in the table.
PRACTICE PROBLEM BASED ON OPEN ADDRESSING-
Problem-
Using the hash function ‘key mod 7’, insert the following sequence of keys in the hash table-
50, 700, 76, 85, 92, 73 and 101
Use linear probing technique for collision resolution.
Solution-
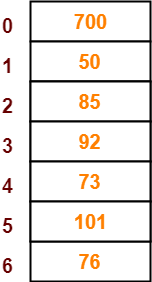
The given sequence of keys will be inserted in the hash table as-
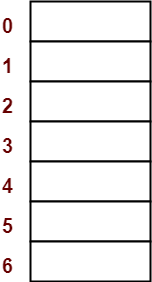
Step-01:
- Draw an empty hash table.
- For the given hash function, the possible range of hash values is [0, 6].
- So, draw an empty hash table consisting of 7 buckets as-
Step-02:
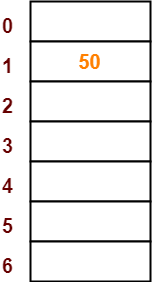
- Insert the given keys in the hash table one by one.
- The first key to be inserted in the hash table = 50.
- Bucket of the hash table to which key 50 maps = 50 mod 7 = 1.
- So, key 50 will be inserted in bucket-1 of the hash table as-
Step-03:
- The next key to be inserted in the hash table = 700.
- Bucket of the hash table to which key 700 maps = 700 mod 7 = 0.
- So, key 700 will be inserted in bucket-0 of the hash table as-
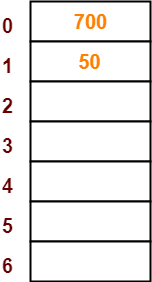
Step-04:
- The next key to be inserted in the hash table = 76.
- Bucket of the hash table to which key 76 maps = 76 mod 7 = 6.
- So, key 76 will be inserted in bucket-6 of the hash table as-
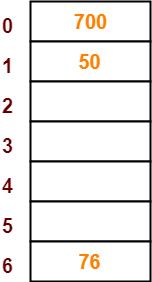
Step-05:
- The next key to be inserted in the hash table = 85.
- Bucket of the hash table to which key 85 maps = 85 mod 7 = 1.
- Since bucket-1 is already occupied, so collision occurs.
- To handle the collision, linear probing technique keeps probing linearly until an empty bucket is found.
- The first empty bucket is bucket-2.
- So, key 85 will be inserted in bucket-2 of the hash table as-
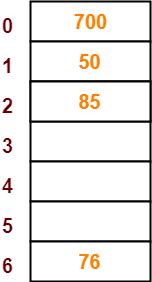
Step-06:
- The next key to be inserted in the hash table = 92.
- Bucket of the hash table to which key 92 maps = 92 mod 7 = 1.
- Since bucket-1 is already occupied, so collision occurs.
- To handle the collision, linear probing technique keeps probing linearly until an empty bucket is found.
- The first empty bucket is bucket-3.
- So, key 92 will be inserted in bucket-3 of the hash table as-
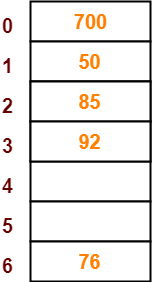
Step-07:
- The next key to be inserted in the hash table = 73.
- Bucket of the hash table to which key 73 maps = 73 mod 7 = 3.
- Since bucket-3 is already occupied, so collision occurs.
- To handle the collision, linear probing technique keeps probing linearly until an empty bucket is found.
- The first empty bucket is bucket-4.
- So, key 73 will be inserted in bucket-4 of the hash table as-
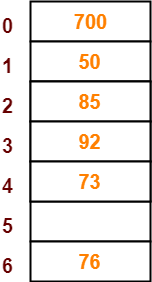
Step-08:
- The next key to be inserted in the hash table = 101.
- Bucket of the hash table to which key 101 maps = 101 mod 7 = 3.
- Since bucket-3 is already occupied, so collision occurs.
- To handle the collision, linear probing technique keeps probing linearly until an empty bucket is found.
- The first empty bucket is bucket-5.
- So, key 101 will be inserted in bucket-5 of the hash table as-
To gain better understanding about Open Addressing,
Next Article- Separate Chaining Vs Open Addressing
Get more notes and other study material of Data Structures.
Watch video lectures by visiting our YouTube channel LearnVidFun.

