Normal Forms in DBMS-
Before you go through this article, make sure that you have gone through the previous article on Normalization in DBMS.
We have discussed-
- Database normalization is a process of making the database consistent.
- Normalization is done through normal forms.
- The standard normal forms generally used are-

In this article, we will discuss some important points about normal forms.
Point-01:
Remember the following diagram which implies-
- A relation in BCNF will surely be in all other normal forms.
- A relation in 3NF will surely be in 2NF and 1NF.
- A relation in 2NF will surely be in 1NF.
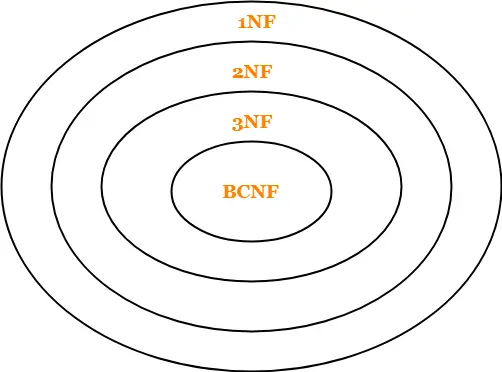
Point-02:
The above diagram also implies-
- BCNF is stricter than 3NF.
- 3NF is stricter than 2NF.
- 2NF is stricter than 1NF.
Point-03:
While determining the normal form of any given relation,
- Start checking from BCNF.
- This is because if it is found to be in BCNF, then it will surely be in all other normal forms.
- If the relation is not in BCNF, then start moving towards the outer circles and check for other normal forms in the order they appear.
Point-04:
- In a relational database, a relation is always in First Normal Form (1NF) at least.
Point-05:
- Singleton keys are those that consist of only a single attribute.
- If all the candidate keys of a relation are singleton candidate keys, then it will always be in 2NF at least.
- This is because there will be no chances of existing any partial dependency.
- The candidate keys will either fully appear or fully disappear from the dependencies.
- Thus, an incomplete candidate key will never determine a non-prime attribute.
Also read- Types of Keys in DBMS
Point-06:
- If all the attributes of a relation are prime attributes, then it will always be in 2NF at least.
- This is because there will be no chances of existing any partial dependency.
- Since there are no non-prime attributes, there will be no Functional Dependency which determines a non-prime attribute.
Point-07:
- If all the attributes of a relation are prime attributes, then it will always be in 3NF at least.
- This is because there will be no chances of existing any transitive dependency for non-prime attributes.
Point-08:
- Third Normal Form (3NF) is considered adequate for normal relational database design.
Point-09:
- Every binary relation (a relation with only two attributes) is always in BCNF.
Point-10:
- BCNF is free from redundancies arising out of functional dependencies (zero redundancy).
Point-11:
- A relation with only trivial functional dependencies is always in BCNF.
- In other words, a relation with no non-trivial functional dependencies is always in BCNF.
Point-12:
- BCNF decomposition is always lossless but not always dependency preserving.
Point-13:
- Sometimes, going for BCNF may not preserve functional dependencies.
- So, go for BCNF only if the lost functional dependencies are not required else normalize till 3NF only.
Point-14:
- There exist many more normal forms even after BCNF like 4NF and more.
- But in the real world database systems, it is generally not required to go beyond BCNF.
Point-15:
- Lossy decomposition is not allowed in 2NF, 3NF and BCNF.
- So, if the decomposition of a relation has been done in such a way that it is lossy, then the decomposition will never be in 2NF, 3NF and BCNF.
Point-16:
- Unlike BCNF, Lossless and dependency preserving decomposition into 3NF and 2NF is always possible.
Point-17:
- A prime attribute can be transitively dependent on a key in a 3NF relation.
- A prime attribute can not be transitively dependent on a key in a BCNF relation.
Point-18:
- If a relation consists of only singleton candidate keys and it is in 3NF, then it must also be in BCNF.
Point-19:
- If a relation consists of only one candidate key and it is in 3NF, then the relation must also be in BCNF.
Also Read- How To Find Candidate Keys?
Next Article- Transactions in DBMS
Get more notes and other study material of Database Management System (DBMS).
Watch video lectures by visiting our YouTube channel LearnVidFun.
Summary

Article Name
Normal Forms in Database | Important Points
DescriptionNormalization in DBMS is a process of making database consistent. Normal Forms in DBMS- First Normal Form (1NF), Second Normal Form (2NF), Third Normal Form (3NF), Boyce Codd Normal Form (BCNF).
Author
Akshay Singhal
Publisher Name

Gate Vidyalay
Publisher Logo
