Process Synchronization-
Before you go through this article, make sure that you have gone through the previous article on Process Synchronization.
We have discussed-
- Process Synchronization provides a synchronization among the processes.
- Synchronization mechanisms allow the processes to access critical section in a synchronized manner.
- This avoids the inconsistent results.
Lock Variable-
- Lock variable is a synchronization mechanism.
- It uses a lock variable to provide the synchronization among the processes executing concurrently.
- However, it completely fails to provide the synchronization.
It is implemented as-
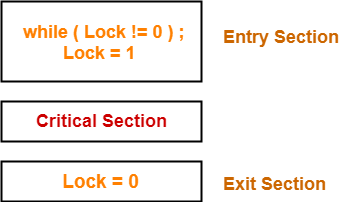
Initially, lock value is set to 0.
- Lock value = 0 means the critical section is currently vacant and no process is present inside it.
- Lock value = 1 means the critical section is currently occupied and a process is present inside it.
Working-
This synchronization mechanism is supposed to work as explained in the following scenes-
Scene-01:
- Process P0 arrives.
- It executes the lock!=0 instruction.
- Since lock value is set to 0, so it returns value 0 to the while loop.
- The while loop condition breaks.
- It sets the lock value to 1 and enters the critical section.
- Now, even if process P0 gets preempted in the middle, no other process can enter the critical section.
- Any other process can enter only after process P0 completes and sets the lock value to 0.
Scene-02:
- Another process P1 arrives.
- It executes the lock!=0 instruction.
- Since lock value is set to 1, so it returns value 1 to the while loop.
- The returned value 1 does not break the while loop condition.
- The process P1 is trapped inside an infinite while loop.
- The while loop keeps the process P1 busy until the lock value becomes 0 and its condition breaks.
Scene-03:
- Process P0 comes out of the critical section and sets the lock value to 0.
- The while loop condition of process P1 breaks.
- It sets the lock value to 1 and enters the critical section.
- Now, even if process P1 gets preempted in the middle, no other process can enter the critical section.
- Any other process can enter only after process P1 completes and sets the lock value to 0.
Failure of the Mechanism-
- The mechanism completely fails to provide the synchronization among the processes.
- It can not even guarantee to meet the basic criterion of mutual exclusion.
Also Read- Criteria For Synchronization Mechanisms
Explanation-
The occurrence of the following scenes may lead to two processes present inside the critical section at the same time-
Scene-01:
- Process P0 arrives.
- It executes the lock!=0 instruction.
- Since lock value is set to 0, so it returns value 0 to the while loop.
- The while loop condition breaks.
- Now, process P0 gets preempted before it sets the lock value to 1.
Scene-02:
- Another process P1 arrives.
- It executes the lock!=0 instruction.
- Since lock value is still 0, so it returns value 0 to the while loop.
- The while loop condition breaks.
- It sets the lock value to 1 and enters the critical section.
- Now, process P1 gets preempted in the middle of the critical section.
Scene-03:
- Process P0 gets scheduled again.
- It resumes its execution.
- Before preemption, it had already failed the while loop condition.
- Now, it begins execution from the next instruction.
- It sets the lock value to 1 (which is already 1) and enters the critical section.
Thus, both the processes get to present inside the critical section at the same time.
Similarly,
- If there are n processes, then all of them may be present inside the critical section at the same time.
- This happens when each process gets preempted immediately after breaking the while loop condition.
Characteristics-
The characteristics of this synchronization mechanism are-
- It can be used for any number of processes.
- It is a software mechanism implemented in user mode.
- There is no support required from the operating system.
- It is a busy waiting solution which keeps the CPU busy when the process is actually waiting.
- It does not fulfill any criteria of synchronization mechanism.
Conclusion-
- The lock variable synchronization mechanism is a complete failure.
- Thus, it is never used.
To gain better understanding about Lock Variable,
Next Article- Test and Set Lock | Synchronization Mechanism
Get more notes and other study material of Operating System.
Watch video lectures by visiting our YouTube channel LearnVidFun.

