Internet Protocol Version 4-
- IPv4 short for Internet Protocol Version 4 is the fourth version of the Internet Protocol (IP).
- IP is responsible to deliver data packets from the source host to the destination host.
- This delivery is solely based on the IP Addresses in the packet headers.
- IPv4 is the first major version of IP.
- IPv4 is a connectionless protocol for use on packet-switched networks.
In this article, we will discuss about IPv4 Header.
IPv4 Header-
The following diagram represents the IPv4 header-
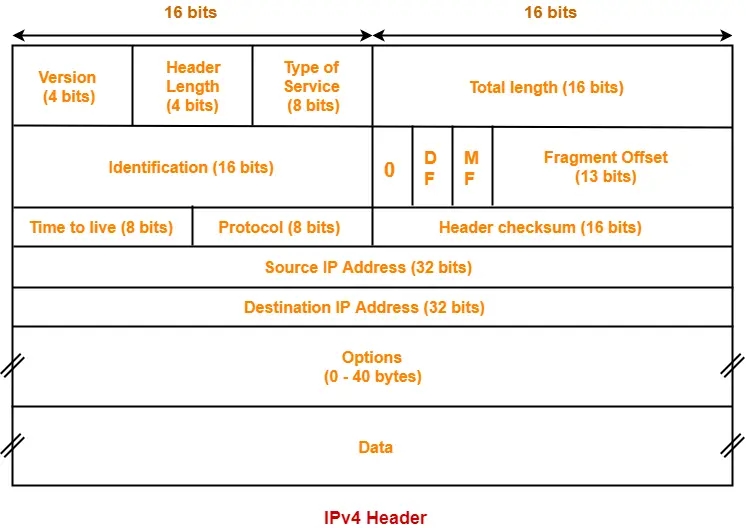
Let us discuss each field of IPv4 header one by one.
1. Version-
- Version is a 4 bit field that indicates the IP version used.
- The most popularly used IP versions are version-4 (IPv4) and version-6 (IPv6).
- Only IPv4 uses the above header.
- So, this field always contains the decimal value 4.
NOTESIt is important to note-
|
2. Header Length-
- Header length is a 4 bit field that contains the length of the IP header.
- It helps in knowing from where the actual data begins.
Minimum And Maximum Header Length-
| The length of IP header always lies in the range-
[20 bytes , 60 bytes] |
- The initial 5 rows of the IP header are always used.
- So, minimum length of IP header = 5 x 4 bytes = 20 bytes.
- The size of the 6th row representing the Options field vary.
- The size of Options field can go up to 40 bytes.
- So, maximum length of IP header = 20 bytes + 40 bytes = 60 bytes.
Concept of Scaling Factor-
- Header length is a 4 bit field.
- So, the range of decimal values that can be represented is [0, 15].
- But the range of header length is [20, 60].
- So, to represent the header length, we use a scaling factor of 4.
In general,
| Header length = Header length field value x 4 bytes |
Examples-
- If header length field contains decimal value 5 (represented as 0101), then-
Header length = 5 x 4 = 20 bytes
- If header length field contains decimal value 10 (represented as 1010), then-
Header length = 10 x 4 = 40 bytes
- If header length field contains decimal value 15 (represented as 1111), then-
Header length = 15 x 4 = 60 bytes
NOTESIt is important to note-
While solving questions-
|
3. Type Of Service-
- Type of service is a 8 bit field that is used for Quality of Service (QoS).
- The datagram is marked for giving a certain treatment using this field.
4. Total Length-
- Total length is a 16 bit field that contains the total length of the datagram (in bytes).
| Total length = Header length + Payload length |
- Minimum total length of datagram = 20 bytes (20 bytes header + 0 bytes data)
- Maximum total length of datagram = Maximum value of 16 bit word = 65535 bytes
5. Identification-
- Identification is a 16 bit field.
- It is used for the identification of the fragments of an original IP datagram.
When an IP datagram is fragmented,
- Each fragmented datagram is assigned the same identification number.
- This number is useful during the re assembly of fragmented datagrams.
- It helps to identify to which IP datagram, the fragmented datagram belongs to.
6. DF Bit-
- DF bit stands for Do Not Fragment bit.
- Its value may be 0 or 1.
When DF bit is set to 0,
- It grants the permission to the intermediate devices to fragment the datagram if required.
When DF bit is set to 1,
- It indicates the intermediate devices not to fragment the IP datagram at any cost.
- If network requires the datagram to be fragmented to travel further but settings does not allow its fragmentation, then it is discarded.
- An error message is sent to the sender saying that the datagram has been discarded due to its settings.
7. MF Bit-
- MF bit stands for More Fragments bit.
- Its value may be 0 or 1.
When MF bit is set to 0,
- It indicates to the receiver that the current datagram is either the last fragment in the set or that it is the only fragment.
When MF bit is set to 1,
- It indicates to the receiver that the current datagram is a fragment of some larger datagram.
- More fragments are following.
- MF bit is set to 1 on all the fragments except the last one.
8. Fragment Offset-
- Fragment Offset is a 13 bit field.
- It indicates the position of a fragmented datagram in the original unfragmented IP datagram.
- The first fragmented datagram has a fragment offset of zero.
| Fragment offset for a given fragmented datagram
= Number of data bytes ahead of it in the original unfragmented datagram |
Concept Of Scaling Factor-
- We use a scaling factor of 8 for the fragment offset.
- Fragment offset field value = Fragment Offset / 8
Need Of Scaling Factor For Fragment Offset
(if no scaling factor is used)
|
9. Time To Live-
- Time to live (TTL) is a 8 bit field.
- It indicates the maximum number of hops a datagram can take to reach the destination.
- The main purpose of TTL is to prevent the IP datagrams from looping around forever in a routing loop.
The value of TTL is decremented by 1 when-
- Datagram takes a hop to any intermediate device having network layer.
- Datagram takes a hop to the destination.
If the value of TTL becomes zero before reaching the destination, then datagram is discarded.
NOTESIt is important to note-
|
10. Protocol-
- Protocol is a 8 bit field.
- It tells the network layer at the destination host to which protocol the IP datagram belongs to.
- In other words, it tells the next level protocol to the network layer at the destination side.
- Protocol number of ICMP is 1, IGMP is 2, TCP is 6 and UDP is 17.
Why Protocol Number Is A Part Of IP Header?
Consider-
In such a case,
ICMP > IGMP > UDP > TCP
If protocol number would have been inside the datagram, then-
That is why, protocol number is made a part of IP header. |
11. Header Checksum-
- Header checksum is a 16 bit field.
- It contains the checksum value of the entire header.
- The checksum value is used for error checking of the header.
At each hop,
- The header checksum is compared with the value contained in this field.
- If header checksum is found to be mismatched, then the datagram is discarded.
- Router updates the checksum field whenever it modifies the datagram header.
The fields that may be modified are-
- TTL
- Options
- Datagram Length
- Header Length
- Fragment Offset
NOTEIt is important to note-
|
Also Read- Checksum
12. Source IP Address-
- Source IP Address is a 32 bit field.
- It contains the logical address of the sender of the datagram.
13. Destination IP Address-
- Destination IP Address is a 32 bit field.
- It contains the logical address of the receiver of the datagram.
14. Options-
- Options is a field whose size vary from 0 bytes to 40 bytes.
- This field is used for several purposes such as-
- Record route
- Source routing
- Padding
1. Record Route-
- A record route option is used to record the IP Address of the routers through which the datagram passes on its way.
- When record route option is set in the options field, IP Address of the router gets recorded in the Options field.
NOTE
Explanation-
|
2. Source Routing-
- A source routing option is used to specify the route that the datagram must take to reach the destination.
- This option is generally used to check whether a certain path is working fine or not.
- Source routing may be loose or strict.
3. Padding-
- Addition of dummy data to fill up unused space in the transmission unit and make it conform to the standard size is called as padding.
- Options field is used for padding.
Example-
- When header length is not a multiple of 4, extra zeroes are padded in the Options field.
- By doing so, header length becomes a multiple of 4.
- If header length = 30 bytes, 2 bytes of dummy data is added to the header.
- This makes header length = 32 bytes.
- Then, the value 32 / 4 = 8 is put in the header length field.
- In worst case, 3 bytes of dummy data might have to be padded to make the header length a multiple of 4.
Also Read- TCP Header | UDP Header
To gain better understanding about IPv4 Header,
Next Article- IP Fragmentation | Examples
Get more notes and other study material of Computer Networks.
Watch video lectures by visiting our YouTube channel LearnVidFun.

