Digital Signatures-
- The signature on a document is the proof to the receiver that the document is coming from the correct entity.
- A digital signature guarantees the authenticity of an electronic document in digital communication.
How Digital Signature Works?
- The sender of the document digitally signs the document.
- The receiver of the document verifies the signature.
The steps involved in the digital signature algorithm are-
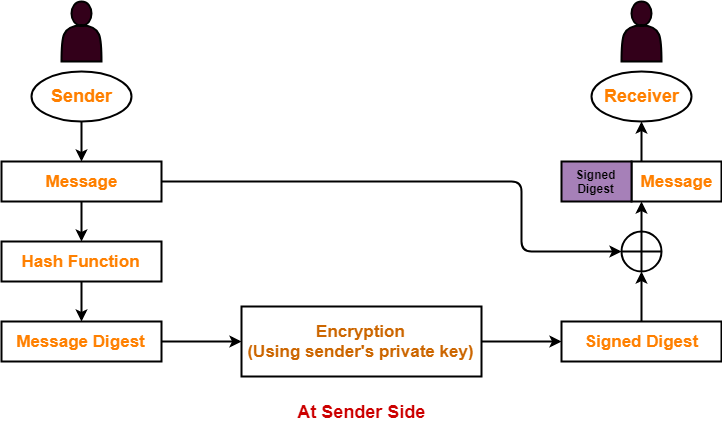
At Sender Side-
At sender side,
- Using a hash function, sender converts the message to be sent into a digested form.
- There are various hash functions that may be used like SHA-1, MD5 etc.
- The message in digested form is called as message digest.
- Sender encrypts the message digest using his private key.
- The encrypted message digest is called as signed digest or signature of the sender.
- Sender sends the signed digest along with the original message to the receiver.
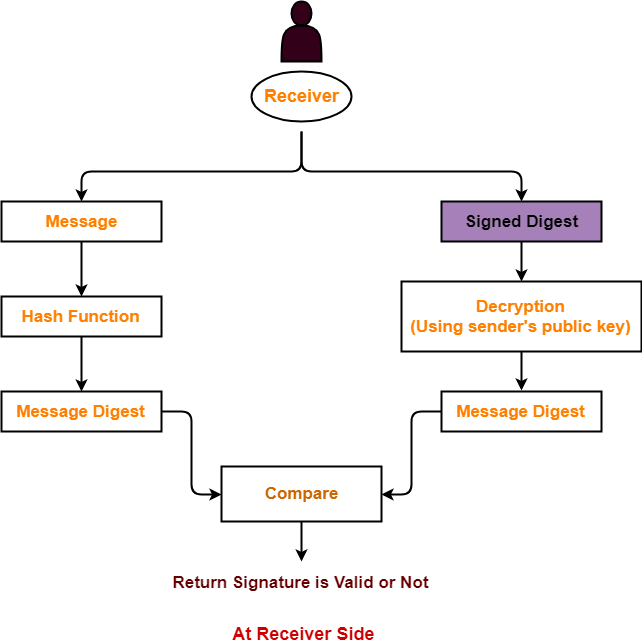
At Receiver Side-
At receiver side,
- Receiver receives the original message and the signed digest.
- Using a hash function, receiver converts the original message into a message digest.
- Also, receiver decrypts the received signed digest using the sender’s public key.
- On decryption, receiver obtains the message digest.
- Now, receiver compares both the message digests.
- If they are same, then it is proved that the document is coming from the correct entity.
Also Read- RSA Algorithm
Important Points-
Point-01:
After digitally signing the document, sender sends the following two things to the receiver-
- Signed digest or signature
- Original message
Point-02:
- Sender uses his private key to digitally sign the document.
- Receiver uses the sender’s public key to verify the signature.
Point-03:
- Digital signature of a person varies from document to document.
- This ensures authenticity of the document.
Point-04:
In digital signature,
- There is one to one relationship between a message and a signature.
- Each message has its own signature.
Point-05:
Digital signature verifies-
- Authenticity
- Integrity
- Non-repudiation
Also Read- Diffie Hellman Key Exchange Algorithm
PRACTICE PROBLEMS BASED ON DIGITAL SIGNATURES-
Problem-01:
Anarkali digitally signs a message and sends it to Salim. Verification of the signature by Salim requires-
- Anarkali’s public key
- Salim’s public key
- Salim’s private key
- Anarkali’s private key
Solution-
Clearly, Option (A) is correct.
Problem-02:
Consider that B wants to send a message m that is digitally signed to A. Let the pair of private and public keys for A and B be denoted by Kx– and Kx+ for x = A, B respectively. Let Kx(m) represent the operation of encrypting m with a key Kx and H(m) represent the message digest. Which one of the following indicates the correct way of sending the message m along with the digital signature to A?
- {m, KB+(H(m))}
- {m, KB–(H(m))}
- {m, KA–(H(m))}
- {m, KA+(H(m))}
Solution-
Clearly, Option (B) is correct.
To gain better understanding about Digital Signatures,
Get more notes and other study material of Computer Networks.
Watch video lectures by visiting our YouTube channel LearnVidFun.

