Application Layer Protocols-
Important application layer protocols are-
- Domain Name Service (DNS)
- Hyper Text Transfer Protocol (HTTP)
- Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP)
- Post Office Protocol (POP)
- File Transfer Protocol (FTP)
In this article, we will discuss about Domain Name Service (DNS).
DNS in Networking-
- DNS is short for Domain Name Service or Domain Name System.
- It is an application layer protocol.
Purpose-
- DNS is a host name to IP Address translation service.
- It converts the names we type in our web browser address bar to the IP Address of web servers hosting those sites.

Need-
The need for Domain Name Service arises due to the following reasons-
Point-01:
- IP Addresses are not static and may change dynamically.
- So, a mapping is required which maps the domain names to the IP Addresses of their web servers.
Point-02:
- IP Addresses are a complex series of numbers.
- So, it is difficult to remember IP Addresses directly while it is easy to remember names.
DNS Resolution-
| DNS Resolution is a process of resolving a domain name onto an IP Address. |
The following diagram illustrates the process of DNS resolution-
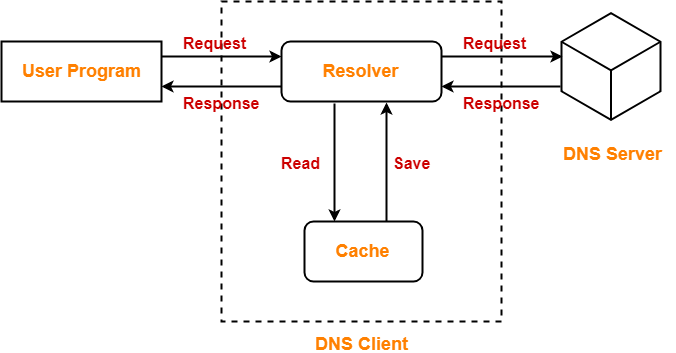
The steps involved in DNS Resolution are-
Step-01:
- A user program sends a name query to a library procedure called the resolver.
Step-02:
Resolver looks up the local domain name cache for a match.
- If a match is found, it sends the corresponding IP Address back.
- If no match is found, it sends a query to the local DNS server.
Step-03:
DNS server looks up the name.
- If a match is found, it returns the corresponding IP Address to the resolver.
- If no match is found, the local DNS server sends a query to a higher level DNS server.
- This process is continued until a result is returned.
Step-04:
- After receiving a response, the DNS client returns the resolution result to the application.
Important Notes-
Note-01:
| DNS uses UDP (port 53) at the transport layer. |
DNS uses UDP at the transport layer due to the following reasons-
Point-01:
- UDP is much faster than TCP.
- TCP is slow as it uses Three-way handshake to start the data transfer.
Point-02:
- DNS requests are very small.
- So, they fits well within UDP segments.
Point-03:
- Although UDP is not reliable but reliability can be added on application layer.
- Reliability can be added by using timeouts and resend at the application layer.
Thus, in the end both speed and protection are achieved.
Note-02:
| DNS is a connection less protocol. |
- DNS uses UDP at the transport layer for replying to the DNS queries of clients.
- Therefore, it is a connection less protocol.
Note-03:
| DNS is non-persistent. |
Note-04:
| DNS is a stateless protocol. |
This is because-
- DNS server accepts the requests, process them, resolves the query and forget about them.
- It does not make any assumption how long this will be.
Note-05:
| Mapping an IP Address onto a domain name is referred to as Inverse domain. |
It is important to note-
- DNS can translate a domain name onto an IP Address.
- Also, it can translate an IP Address onto a domain name.
Note-06:
| For the first time,
There is more delay in translating the domain name onto an IP Address. |
- Converting a domain name onto an IP Address is an extra overhead.
- This overhead is called as DNS Overhead.
- It causes an unnecessary delay in serving the request.
- So, there is more delay for the first time.
- To reduce the delay next time, IP Addresses are stored in the computer using log.
- This avoids the DNS overhead next time and takes less time in serving the request.
- When it gets expired, the request is again served through DNS.
To gain better understanding about Domain Name Service,
Next Article- Hyper Text Transfer Protocol | HTTP
Get more notes and other study material of Computer Networks.
Watch video lectures by visiting our YouTube channel LearnVidFun.

