Critical Section-
Before you go through this article, make sure that you have gone through the previous article on Process Synchronization.
We have discussed-
- Process Synchronization controls the execution of processes running concurrently so as to produce the consistent results.
- Critical section is a part of the program where shared resources are accessed by the process.
Critical Section Problem-
- If multiple processes access the critical section concurrently, then results produced might be inconsistent.
- This problem is called as critical section problem.
Synchronization Mechanisms-
| Synchronization mechanisms allow the processes to access critical section in a synchronized manner to avoid the inconsistent results. |
For every critical section in the program, a synchronization mechanism adds-
- An entry section before the critical section
- An exit section after the critical section
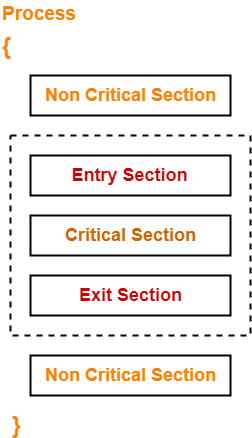
Entry Section-
- It acts as a gateway for a process to enter inside the critical section.
- It ensures that only one process is present inside the critical section at any time.
- It does not allow any other process to enter inside the critical section if one process is already present inside it.
Exit Section-
- It acts as an exit gate for a process to leave the critical section.
- When a process takes exit from the critical section, some changes are made so that other processes can enter inside the critical section.
Criteria For Synchronization Mechanisms-
Any synchronization mechanism proposed to handle the critical section problem should meet the following criteria-
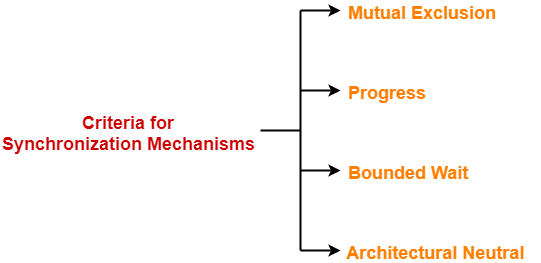
- Mutual Exclusion
- Progress
- Bounded Wait
- Architectural Neutral
1. Mutual Exclusion-
The mechanism must ensure-
- The processes access the critical section in a mutual exclusive manner.
- Only one process is present inside the critical section at any time.
- No other process can enter the critical section until the process already present inside it completes.
2. Progress-
The mechanism must ensure-
- An entry of a process inside the critical section is not dependent on the entry of another process inside the critical section.
- A process can freely enter inside the critical section if there is no other process present inside it.
- A process enters the critical section only if it wants to enter.
- A process is not forced to enter inside the critical section if it does not want to enter.
3. Bounded Wait-
The mechanism should ensure-
- The wait of a process to enter the critical section is bounded.
- A process gets to enter the critical section before its wait gets over.
4. Architectural Neutral-
The mechanism should ensure-
- It can run on any architecture without any problem.
- There is no dependency on the architecture.
Important Notes-
Note-01:
- Mutual Exclusion and Progress are the mandatory criteria.
- They must be fulfilled by all the synchronization mechanisms.
Note-02:
- Bounded waiting and Architectural neutrality are the optional criteria.
- However, it is recommended to meet these criteria if possible.
To gain better understanding of Critical Section in OS,
Next Article- Lock Variable | Synchronization Mechanism
Get more notes and other study material of Operating System.
Watch video lectures by visiting our YouTube channel LearnVidFun.
Summary

Article Name
Critical Section | Critical Section Problem
DescriptionCritical Section in OS is a part of the program where shared resources are accessed by the processes. Critical Section Problem arises when multiple processes access the critical section at the same time.
Author
Akshay Singhal
Publisher Name

Gate Vidyalay
Publisher Logo
