Contiguous Memory Allocation-
- Contiguous memory allocation is a memory allocation technique.
- It allows to store the process only in a contiguous fashion.
- Thus, entire process has to be stored as a single entity at one place inside the memory.
Techniques-
There are two popular techniques used for contiguous memory allocation-
- Static Partitioning
- Dynamic Partitioning
In this article, we will discuss about Static Partitioning.
Static Partitioning-
- Static partitioning is a fixed size partitioning scheme.
- In this technique, main memory is pre-divided into fixed size partitions.
- The size of each partition is fixed and can not be changed.
- Each partition is allowed to store only one process.
Example-
Under fixed size partitioning scheme, a memory of size 10 KB may be divided into fixed size partitions as-
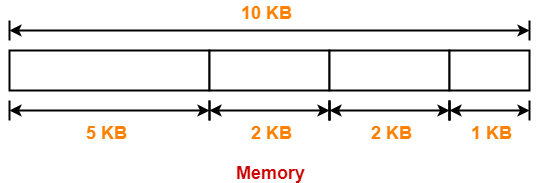
- These partitions are allocated to the processes as they arrive.
- The partition allocated to the arrived process depends on the algorithm followed.
Algorithms for Partition Allocation-
Popular algorithms used for allocating the partitions to the arriving processes are-
- First Fit Algorithm
- Best Fit Algorithm
- Worst Fit Algorithm
1. First Fit Algorithm-
- This algorithm starts scanning the partitions serially from the starting.
- When an empty partition that is big enough to store the process is found, it is allocated to the process.
- Obviously, the partition size has to be greater than or at least equal to the process size.
2. Best Fit Algorithm-
- This algorithm first scans all the empty partitions.
- It then allocates the smallest size partition to the process.
3. Worst Fit Algorithm-
- This algorithm first scans all the empty partitions.
- It then allocates the largest size partition to the process.
Important Points-
Point-01:
For static partitioning,
- Best Fit Algorithm works best.
- This is because space left after the allocation inside the partition is of very small size.
- Thus, internal fragmentation is least.
Point-02:
For static partitioning,
- Worst Fit Algorithm works worst.
- This is because space left after the allocation inside the partition is of very large size.
- Thus, internal fragmentation is maximum.
Internal Fragmentation
External Fragmentation
|
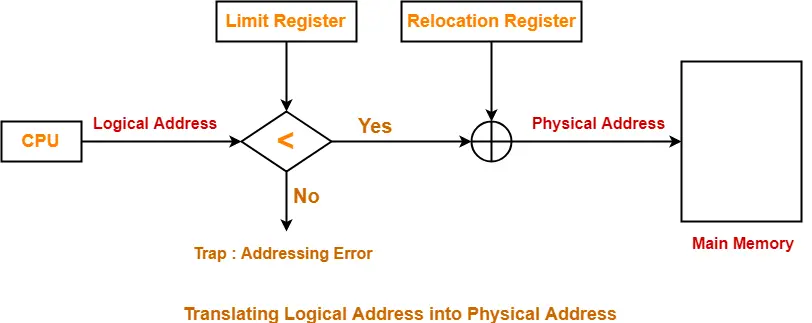
Translating Logical Address into Physical Address-
- CPU always generates a logical address.
- A physical address is needed to access the main memory.
Following steps are followed to translate logical address into physical address-
Step-01:
- The translation scheme uses two registers that are under the control of operating system.
- During context switching, the values corresponding to the process being loaded are set in the registers.
These two registers are-
- Relocation Register
- Limit Register
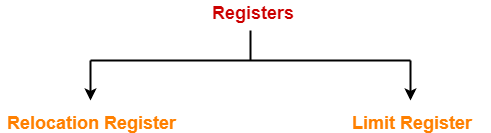
- Relocation Register stores the base address or starting address of the process in the main memory.
- Limit Register stores the size or length of the process.
Step-02:
- CPU generates a logical address containing the address of the instruction that it wants to read.
Step-03:
- The logical address generated by the CPU is compared with the limit of the process.
- Now, two cases are possible-
Case-01: Generated Address >= Limit
- If address is found to be greater than or equal to the limit, a trap is generated.
- This helps to prevent unauthorized access.
Case-02: Generated Address < Limit
- The address must always lie in the range [0, limit-1].
- If address is found to be smaller than the limit, then the request is treated as a valid request.
- Then, generated address is added with the base address of the process.
- The result obtained after addition is the address of the memory location storing the required word.
Diagram-
The following diagram illustrates the above steps of translating logical address into physical address-
Advantages-
The advantages of static partitioning are-
- It is simple and easy to implement.
- It supports multiprogramming since multiple processes can be stored inside the main memory.
- Only one memory access is required which reduces the access time.
Disadvantages-
The disadvantages of static partitioning are-
- It suffers from both internal fragmentation and external fragmentation.
- It utilizes memory inefficiently.
- The degree of multiprogramming is limited equal to number of partitions.
- There is a limitation on the size of process since processes with size greater than the size of largest partition can’t be stored and executed.
To gain better understanding about Contiguous Memory Allocation,
Next Article- Dynamic Partitioning
Get more notes and other study material of Operating System.
Watch video lectures by visiting our YouTube channel LearnVidFun.

