Application Layer Protocols-
Important application layer protocols are-
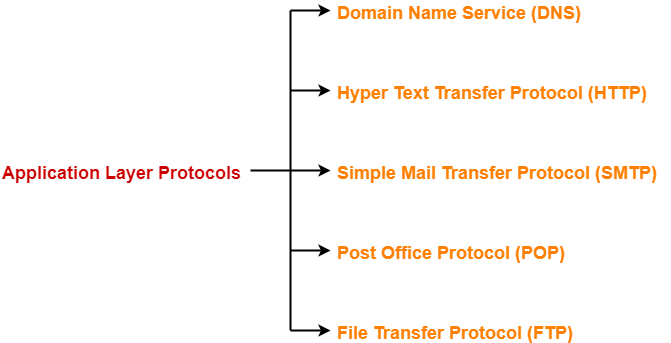
- Domain Name Service (DNS)
- Hyper Text Transfer Protocol (HTTP)
- Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP)
- Post Office Protocol (POP)
- File Transfer Protocol (FTP)
In this article, we will discuss about Hyper Text Transfer Protocol (HTTP).
Hyper Text Transfer Protocol-
- HTTP is short for Hyper Text Transfer Protocol.
- It is an application layer protocol.
Purpose-
- It is mainly used for the retrieval of data from websites throughout the internet.
- It works on the top of TCP/IP suite of protocols.
Working-
HTTP uses a client-server model where-
- Web browser is the client.
- Client communicates with the web server hosting the website.
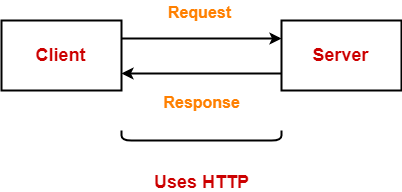
Whenever a client requests some information (say clicks on a hyperlink) to the website server.
The browser sends a request message to the HTTP server for the requested objects.
Then-
- HTTP opens a connection between the client and server through TCP.
- HTTP sends a request to the server which collects the requested data.
- HTTP sends the response with the objects back to the client.
- HTTP closes the connection.
HTTP Connections-
HTTP connections can be of two types-
- Non-persistent HTTP connection
- Persistent HTTP connection
| Non-persistent HTTP connection | Persistent HTTP connection |
| Non-persistent HTTP connection is one that is used for serving exactly one request and sending one response. | Persistent HTTP connection is one that can be used for serving multiple requests. |
| HTTP server closes the TCP connection automatically after sending a HTTP response. | HTTP server closes the TCP connection only when it is not used for a certain configurable amount of time. |
| A new separate TCP connection is used for each object. | A single TCP connection is used for sending multiple objects one after the other. |
| HTTP 1.0 supports non-persistent connections by default. | HTTP 1.1 supports persistent connections by default. |
Example-
Suppose a request has been made for a HTML page that contains 10 images (called objects). Then, With non-persistent connection, all the 11 objects (1 page + 10 images) will be sent one by one. For getting each object, a new separate connection will be opened and used. |
Example-
Suppose a request has been made for a HTML page that contains 10 images (called objects). Then, With persistent connection, all the 11 objects (1 page + 10 images) will be sent one after the other using a single TCP connection.
|
Important Notes-
Note-01:
| HTTP uses TCP at the transport layer. |
This is because-
- Unlike UDP, it guarantees the delivery of data via a Three-way handshake.
- It ensures the re transmission of lost packets.
- HTTP does not have any inbuilt facility for providing reliability.
- So, if HTTP uses UDP, then it will have to maintain or handle the session on its own.
- For example- If a packet gets lost, then HTTP will have to re-transmit the packet.
Note-02:
It is important to know-
- Any service which does not use TCP should have the inbuilt facility for providing reliability.
Note-03:
| HTTP uses port number 80. |
- HTTP clients uses port 80 to send and receive requested web pages from a HTTP server.
- Similarly, HTTP server responds to all the requests at port 80.
Note-04:
| HTTP 1.0 is non-persistent and HTTP 1.1 is persistent. |
- Already discussed in the above table.
- Persistent connections improve the performance by 20%.
Note-05:
| HTTP 1.0 is a connectionless protocol. |
This is because-
- After serving the single HTTP request, the connection is closed and it is not used again.
- So, HTTP 1.0 without connection keep alive is connectionless.
Note-06:
| HTTP is an in-band protocol. |
This is because-
- HTTP passes the control data (commands) and main data over the same connection.
- Both control data and main data are processed in the same way without any distinction.
- No high priority is given to the control data (commands).
Note-07:
| HTTP is a stateless protocol. |
This is because-
- HTTP server does not maintain any state.
- It forgets about the client after sending the response.
- It treats every new request independently.
- HTTP closes the connection automatically after generating the response for each request.
- This ensures that no client can engage connection with web server for a long time.
What If HTTP Is Stateful Protocol?
If HTTP is a stateful protocol, then-
|
To gain better understanding about HTTP Protocol,
Next Article- Simple Mail Transfer Protocol | SMTP
Get more notes and other study material of Computer Networks.
Watch video lectures by visiting our YouTube channel LearnVidFun.