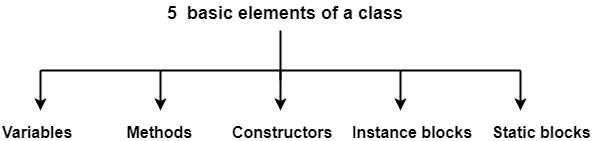
Elements of a class-
Java is a class based language where the entire code is written inside a class.
Any class written in Java consists of the following 5 elements-
- Variables
- Methods
- Constructors
- Instance blocks
- Static blocks
In this post, we will discuss about the methods of Java in detail.
Methods in Java-
Method is an element of a class that is used for writing the logic of the program as it is not allowed to write the logic of the program directly inside a class.
Example-
Writing the logic for addition of two numbers as shown below is not allowed-
class Test
{
int a = 50;
int b = 100;
System.out.println(a+b);
}
The logic for addition of two numbers has to be written using a method as shown below-
class Test
{
int a = 50;
int b = 100;
void add( )
{
System.out.println(a+b);
}
}
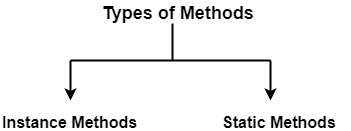
Types of Methods in Java-
There are mainly two types of methods in Java-
- Instance methods
- Static methods
1. Instance Methods-
- The methods that are associated with the objects of the class and not to the class as a whole are called as instance methods.
- Every individual object owns its unique copy of all the instance methods belonging to that class.
- The call made to the instance methods is resolved at run time through dynamic binding.
- Overriding of instance methods is allowed.
How to access instance methods?
Just like instance variables,
- Instance methods can be called directly inside the instance area.
- Instance methods can not be called directly inside the static area and necessarily requires an object reference for calling them.
2. Static Methods-
- The methods that are associated with the entire class and not to the individual objects are called as static methods.
- A single copy gets created for the static methods and this single copy is shared by all the objects belonging to that class.
- Static methods are declared with the ‘static’ modifier.
- The call made to the static methods is resolved at compile time through static binding by the compiler.
- Overriding of static methods is not at all allowed.
- Static methods can be used to write the code that is common and is meant to be shared among all the instances.
Since, static methods are associated with the entire class, they are popularly called as class methods.
How to access static methods?
Just like static variables,
- Static methods can be called by using class name and dot operator. (Recommended)
- Static methods can be called directly within the same package.
- Static methods can be called by using object reference and dot operator.
NOTE-
- Although static methods can be accessed using object reference and dot operator but it is not recommended because it does not make it clear that we are talking about the class methods.
Always make a habit of calling the static methods by using class name and dot operator.
Difference between Instance methods and Static methods-
| Instance Methods | Static Methods |
| Instance methods are associated with the objects of the class and not to the class as a whole. | Static methods are associated with the entire class and not to the individual objects. |
| Every individual object owns its unique copy of all the instance methods belonging that class. | A single copy gets created for the static methods and this single copy is shared by all the objects associated to that class. |
| The call made to the instance methods is resolved at run time through dynamic binding. | The call made to the static methods is resolved at compile time through static binding by the compiler. |
| Overriding of instance methods is allowed. | Overriding of static methods is not at all allowed. |
Important rules you must know about methods in Java-
Rule-01:
As in any other programming language, it is perfectly allowed to define your own methods in Java known as “user defined methods”.
Syntax-
modifiers_list return_type method_name (param_list) throws Exception
{
//method body
}
Rule-02:
It is compulsory to mention the return type when defining methods in Java.
Example- 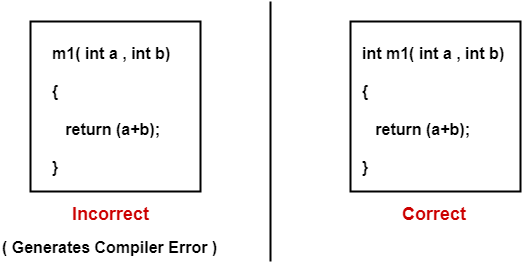
Rule-03:
Calling a method from another method is perfectly allowed in Java.
Example-
class Test
{
void m1( )
{
m2( ); // call to method m2( ) from method m1( )
System.out.println("m1 method called");
}
void m2( )
{
System.out.println("m2 method called");
}
public static void main(String[ ] args)
{
Test t = new Test( ); // Object creation
t.m1( ); // Call to method m1( ) from main method
}
}
Rule-04:
Inside a class, two methods with the same signatures (duplicate methods) are not allowed even if their return types are different.
|
NOTE Method signature includes only these two things- method name and parameter list. |
Rule-05:
Declaring a method inside another method is called as inner method. Inner methods are not allowed in Java. However, the concept of Inner classes is fully supported by Java.
Rule-06:
Inside static methods, ‘this‘ keyword is not allowed (static area) as there is no instance for ‘this’ to refer to inside static methods.
Rule-07:
Static methods must be given implementation (at least empty implementation) otherwise compile time error will be generated.
Example-

Examples based on using methods in Java-
Example-01:
class Test
{
void m1( ) // Instance Method
{
System.out.println("m1 method called");
}
static void m2( ) // Static Method
{
System.out.println("m2 method called");
}
public static void main(String[ ] args)
{
Test t = new Test( ); // Object Creation
t.m1( ); // Call to instance method m1( ) using object reference
Test.m2( ); // Call to static method m2( ) using class name and dot operator
}
}
OUTPUT-
m1 method called m2 method called
Example-02:
class Test
{
void m1(int a , char ch) // Instance Method
{
System.out.println("m1 method called");
System.out.println(a);
System.out.println(ch);
}
static void m2(String str , double d) // Static Method
{
System.out.println("m2 method called");
System.out.println(str);
System.out.println(d);
}
public static void main(String[ ] args)
{
Test t = new Test( ); // Object Creation
t.m1(50,'G'); // Call to instance method m1( ) using object reference
Test.m2("Gate Vidyalay",50.5); // Call to static method m2( ) using class name and dot operator
}
}
OUTPUT-
m1 method called 50 G m2 method called Gate Vidyalay 50.5
Get more notes and other study material of Core Java.
Watch video lectures by visiting our YouTube channel LearnVidFun.