Cache Memory-
Before you go through this article, make sure that you have gone through the previous article on Cache Memory.
We have discussed-
| Cache memory bridges the speed mismatch between the processor and the main memory. |
When cache hit occurs,
- The required word is present in the cache memory.
- The required word is delivered to the CPU from the cache memory.
When cache miss occurs,
- The required word is not present in the cache memory.
- The page containing the required word has to be mapped from the main memory.
- This mapping is performed using cache mapping techniques.
In this article, we will discuss different cache mapping techniques.
Cache Mapping-
- Cache mapping defines how a block from the main memory is mapped to the cache memory in case of a cache miss.
OR
- Cache mapping is a technique by which the contents of main memory are brought into the cache memory.
The following diagram illustrates the mapping process-
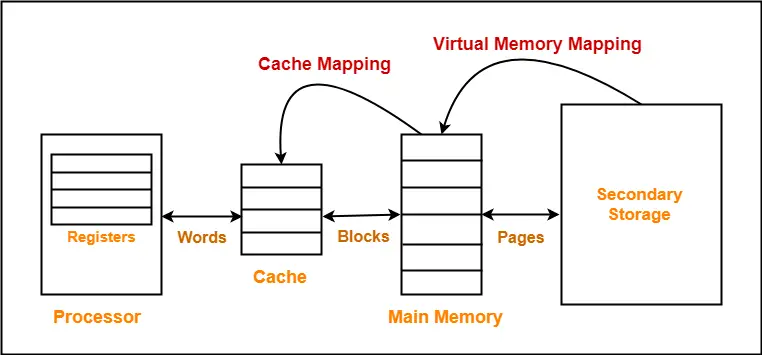
Now, before proceeding further, it is important to note the following points-
NOTES
|
Cache Mapping Techniques-
Cache mapping is performed using following three different techniques-
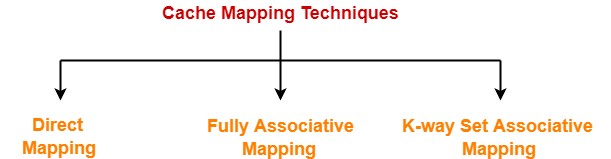
- Direct Mapping
- Fully Associative Mapping
- K-way Set Associative Mapping
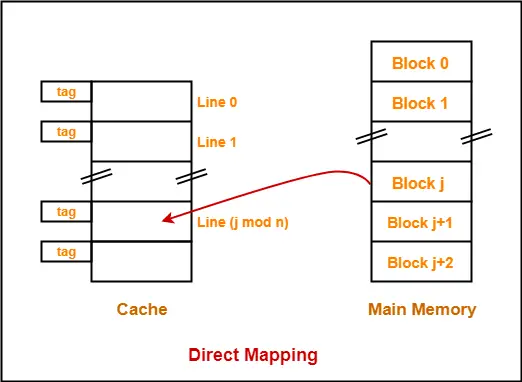
1. Direct Mapping-
In direct mapping,
- A particular block of main memory can map only to a particular line of the cache.
- The line number of cache to which a particular block can map is given by-
|
Cache line number
= ( Main Memory Block Address ) Modulo (Number of lines in Cache) |
Example-
- Consider cache memory is divided into ‘n’ number of lines.
- Then, block ‘j’ of main memory can map to line number (j mod n) only of the cache.
Need of Replacement Algorithm-
In direct mapping,
- There is no need of any replacement algorithm.
- This is because a main memory block can map only to a particular line of the cache.
- Thus, the new incoming block will always replace the existing block (if any) in that particular line.
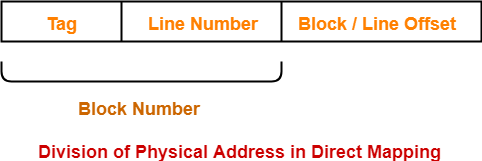
Division of Physical Address-
In direct mapping, the physical address is divided as-
2. Fully Associative Mapping-
In fully associative mapping,
- A block of main memory can map to any line of the cache that is freely available at that moment.
- This makes fully associative mapping more flexible than direct mapping.
Example-
Consider the following scenario-
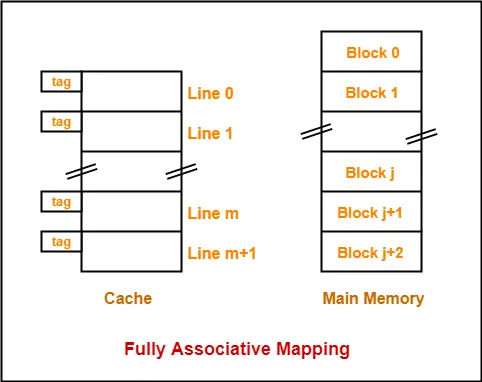
Here,
- All the lines of cache are freely available.
- Thus, any block of main memory can map to any line of the cache.
- Had all the cache lines been occupied, then one of the existing blocks will have to be replaced.
Need of Replacement Algorithm-
In fully associative mapping,
- A replacement algorithm is required.
- Replacement algorithm suggests the block to be replaced if all the cache lines are occupied.
- Thus, replacement algorithm like FCFS Algorithm, LRU Algorithm etc is employed.
Division of Physical Address-
In fully associative mapping, the physical address is divided as-

3. K-way Set Associative Mapping-
In k-way set associative mapping,
- Cache lines are grouped into sets where each set contains k number of lines.
- A particular block of main memory can map to only one particular set of the cache.
- However, within that set, the memory block can map any cache line that is freely available.
- The set of the cache to which a particular block of the main memory can map is given by-
|
Cache set number
= ( Main Memory Block Address ) Modulo (Number of sets in Cache) |
Also Read- Set Associative Mapping | Implementation and Formulas
Example-
Consider the following example of 2-way set associative mapping-
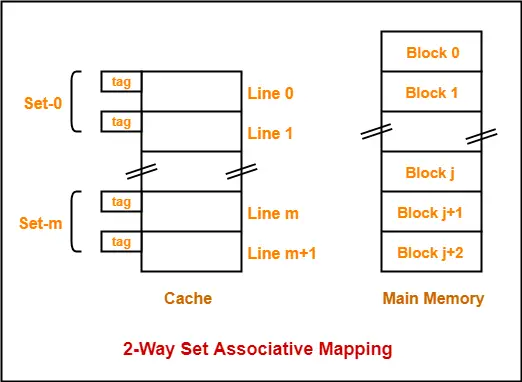
Here,
- k = 2 suggests that each set contains two cache lines.
- Since cache contains 6 lines, so number of sets in the cache = 6 / 2 = 3 sets.
- Block ‘j’ of main memory can map to set number (j mod 3) only of the cache.
- Within that set, block ‘j’ can map to any cache line that is freely available at that moment.
- If all the cache lines are occupied, then one of the existing blocks will have to be replaced.
Need of Replacement Algorithm-
- Set associative mapping is a combination of direct mapping and fully associative mapping.
- It uses fully associative mapping within each set.
- Thus, set associative mapping requires a replacement algorithm.
Division of Physical Address-
In set associative mapping, the physical address is divided as-

Special Cases-
- If k = 1, then k-way set associative mapping becomes direct mapping i.e.
| 1-way Set Associative Mapping ≡ Direct Mapping |
- If k = Total number of lines in the cache, then k-way set associative mapping becomes fully associative mapping.
Next Article- Direct Mapping | Implementation & Formulas
Get more notes and other study material of Computer Organization and Architecture.
Watch video lectures by visiting our YouTube channel LearnVidFun.

